What Is Cloud Application Development?
Cloud computing is considered the best possible approach to cost reduction and giving companies more opportunities to grow.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article was authored by Brocoder Rodion Salnik and published with permission.
Cloud-based application development makes data collection more convenient and simplifies security and management. It also allows enterprises to create productivity-based applications to enhance customer experience and revenue. Additionally, cloud software development solutions enable businesses to invest in low-code app development, which is also a time- and cost-effective process.
![Source: https://www.researchandmarkets.com/]() Cloud Applications Prospectives
Cloud Applications Prospectives
Cloud apps and services are now used by almost everyone. According to recent statistics, 50% of the world’s corporate data is stored in the cloud, while 90% of large enterprises have adopted a multi-cloud infrastructure. Cloud solutions bring multi-experience to businesses, which is considered a future of application development, especially when using technologies like cloud computing, AI/ML (Artificial intelligence/ Machine Learning), and IoT (Internet of Things). The conversational and seamless experience with mobile apps and a range of other business benefits are the main drivers of the growing adoption and popularity of cloud applications among organizations.
Cloud is the powerhouse that drives today’s digital organizations.
Sid Nag
VP Analyst, Gartner
According to Gartner, worldwide end-user spending on public cloud services is projected to grow to $494.7 billion in 2022 from $410.9 billion in 2021, representing an increase of 20.4%. At the same time, in 2023, end-user spending is projected to reach nearly $600 billion. The global infrastructure as a service (IaaS) market continues to grow steadily as cloud-native becomes the primary architecture for most modern workloads. Cloud supports the scalability and composability required by advanced technologies and applications while enabling enterprises to address emerging needs, such as data integration, enhanced customer experience, and sovereignty.
In 2021, the top 5 IaaS providers accounted for over 80% of the market, with Google Cloud seeing the highest growth rate of the top vendors in the 2020-2021 period.
| COMPANY | 2020 MARKET SHARE (%) | 2020 MARKET SHARE (%) | 2020-2021 GROWTH (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | 40.8 | 38.9 | 35.0 |
| Microsoft | 19.7 | 21.1 | 51.3 |
| Alibaba | 9.5 | 9.5 | 41.9 |
| 6.1 | 7.1 | 63.7 | |
| Huawei | 4.2 | 4.6 | 56.3 |
Gartner's research also predicts enterprise IT spending on public cloud computing to overtake spending on traditional IT in 2025, with 51% of IT spending in categories such as application software, infrastructure software, system infrastructure markets, and business process services will move from traditional solutions to the public cloud by 2025. According to analysts, 65.9% of application software spending will be directed to cloud technologies in 2025, compared to 57.7% in 2022.
By the end of 2022, traditional offerings will account for 58.7% of the addressable revenue, but growth in traditional markets is expected to be much lower than in the cloud. Demand for agile work processes, composable architecture, and integration capabilities will fuel the move to the cloud.
The Scale of Global Cloud Computing, 2019-2025
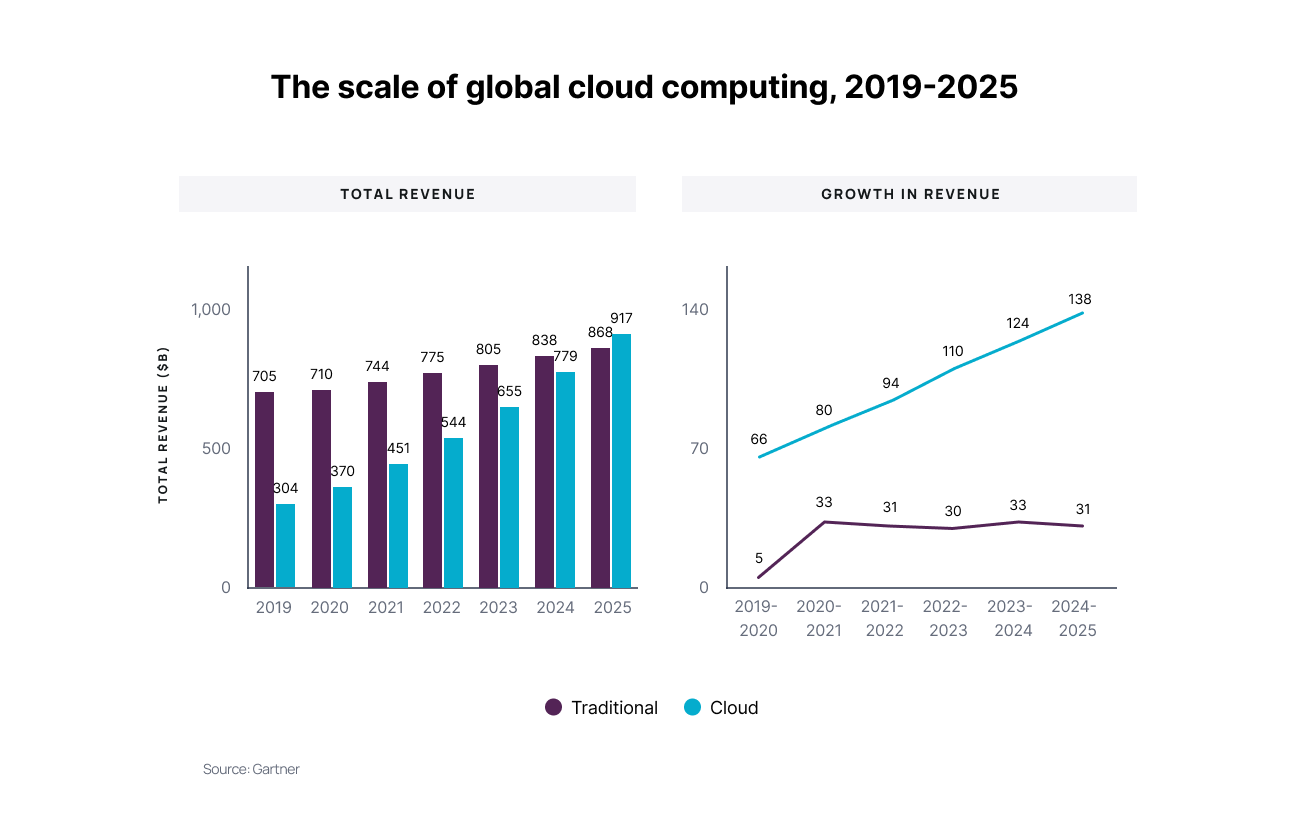 Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is forecast to experience the highest end-user spending growth in 2023 at 30.5%, followed by platform-as-a-service (PaaS) at 24.4% and desktop-as-a-service (DaaS) at 23.7%. SaaS remains the largest public cloud services market segment, forecasted to reach $208 billion in end-user spending in 2023. Analysts expect steady velocity within this segment as enterprises choose multiple paths to market with SaaS, such as through cloud marketplaces, and continue to break up large, monolithic apps into composable parts for more efficient DevOps processes.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is forecast to experience the highest end-user spending growth in 2023 at 30.5%, followed by platform-as-a-service (PaaS) at 24.4% and desktop-as-a-service (DaaS) at 23.7%. SaaS remains the largest public cloud services market segment, forecasted to reach $208 billion in end-user spending in 2023. Analysts expect steady velocity within this segment as enterprises choose multiple paths to market with SaaS, such as through cloud marketplaces, and continue to break up large, monolithic apps into composable parts for more efficient DevOps processes.
The cloud shift is prompting organizations to move away from powering their workforce with traditional client computing solutions, such as desktops and other physical in-office tools. Organizations are widely adopting cloud computing services as they provide valuable insights into partnering tactics, investments, go-to-market approaches, alliance and acquisition strategies, and best operational practices, helping to measure, correlate, and analyze business activities and ensure that company operations meet customer requirements. All of this, along with numerous benefits of the cloud for businesses, is expected to keep driving the cloud computing market growth and accelerate its adoption rate across many industries.
What Is a Cloud-Based App?
Cloud computing technology involves delivering various services and resources, such as data storage, servers, and databases online, with the cloud vendor providing computing reserves on a paid basis or for free. Cloud services allow businesses to employ the needed services, resources, and space to store data without maintaining the infrastructure. Companies can perform massive calculations and deliver top services thanks to the ability to process large amounts of data through third-party-owned IT infrastructure.
Cloud-based applications or cloud apps are software products that distribute the data storage and processing logic on a gadget between the client and server sides. The client-side is visible to the user and accessible to interact with, while the server side is responsible for processing data. Cloud applications can be characterized as follows:
- Cloud-based apps can be accessed via any Internet-connected device, like a smartphone, tablet, or desktop, allowing the user to be independent of browser capacities.
- The application’s data is stored in the cloud and can be partly cached on a user’s device, which means that there are minimum device requirements for the application to work.
- The cloud infrastructure may temporarily store information on the user’s device to provide access to it while offline. Once the user is online, the app is updated and uploads generated data from offline mode to the cloud storage.
- You can set up backup schedules, compression, data optimization, and encryption in any way you want.
- Cloud-based apps offer users access to third-party cloud computing services with API integration and are easier to set up than web applications.
Cloud application development offers numerous benefits for businesses, some of which include the following:
- Improved application performance. The more computations are performed on the app’s server-side — the faster and more reliable the service for users will be.
- Scalability. Businesses can hire processing power when needed, which is very convenient at times of high demand for computing power.
- Security. Cloud services reduce the risk of physical IT infrastructure failure.
- Increased uptime. With the reliability of cloud services, a cloud app will stay up more quickly and efficiently than through your own IT infrastructure.
- Easy software update. Using cloud technology, you can easily update your app through mass deployment.
Types of Cloud-Based Solutions Available for Enterprises
Cloud computing technologies include various services and resources, such as storage, databases, data servers, etc., that are run by third parties. The third-party provides the computer reserves on a paid or free basis, allowing you to use the space, services, and resources without worrying about infrastructure maintenance. There are four common cloud types available for enterprises:
- Private cloud. The cloud functions as a private web-based system with a secure space for data, apps, users, and the web. A private cloud is solely dedicated to a single end-user or group of users, where the environment usually runs behind that group or user's firewall. There are also some private cloud subtypes, including:
- Managed private clouds. Customers create and use a private cloud, which is deployed, configured, and managed by a third-party vendor. This subtype of private cloud helps enterprises with underskilled or understaffed IT teams provide better private cloud infrastructure and services.
- Dedicated clouds. This subtype represents a cloud within another cloud. Users can have a dedicated cloud on a private or public cloud. For example, the accounting department may have its own dedicated cloud within the organization's cloud.
- Public cloud. Data in the public cloud can be accessed online via any authorized device. This cloud usually has optimal data storage prices and data processing flexibility, making it a popular choice among users. Some of the top public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Alibaba Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud.
- Hybrid cloud. Hybrid cloud services are considered both public and private. It is a seemingly single IT environment created from multiple environments connected through local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), virtual private networks (VPNs), and APIs. Every IT system becomes a hybrid cloud where applications can move in and out of multiple separate yet connected environments. At least a few of these environments must come from consolidated IT resources that can scale on demand. With a hybrid cloud, IT companies can distribute data among on-device services and third-party apps, finding additional options for deployment and optimization.
- Community cloud (Multi-cloud). This type of cloud service is similar to the private cloud — the only difference here is that the data sharing is between multiple organizations from a particular community with common concerns like security, jurisdiction, and compliance. All hybrid clouds are multi-clouds, but, at the same time, not all multi-clouds are hybrid clouds. Multi-clouds become hybrid clouds when they are connected by some form of integration or orchestration.
All these cloud types abstract, aggregate, and share scalable computing resources across the network, enabling cloud computing. Every cloud is created using a mix of technologies, which includes an operating system, management platform, and application programming interfaces (APIs). Automation and virtualization software can also be added to every type of cloud for additional capabilities or increased efficiency.
Main Types of Cloud-Based Apps: SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS
Cloud services represent software, infrastructure, or platforms hosted by third-party vendors and available to users through the internet. There are three types of as-a-service cloud app development solutions — SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS. Each of them facilitates the user data flow from front-end clients through the internet to and from the cloud service provider’s systems but varies what is being provided.
Software as a Service or SaaS
Software as a service is a service that delivers a software application managed by a cloud service provider to its users. Typically, SaaS applications are web or mobile apps that users can access through a web browser. SaaS eliminates the need to configure or install apps on the device, providing more methods for group access to the software. Bug fixes, software updates, and other general software maintenance are performed for the user by the cloud service vendor, and they connect to the cloud applications through a dashboard or API. Software as a service cloud application development can be used for:
- Managing CRM systems and client databases;
- Providing auditing features and email tools;
- Automating services and products sign-up;
- Managing documents for file sharing and collaboration;
- Sharing calendars and agendas across the organization to plan future events.
To date, the TOP SaaS companies include Salesforce, Microsoft, Adobe Creative Cloud, Google Workspace, Zendesk, and others.
Platform as a Service or PaaS
PaaS means the hardware and software platform is provided and managed by a cloud service provider, with the user handling the applications running on the platform and the data the apps rely on. This cloud service provides a shared platform for application development and management without the need to create and maintain the infrastructure usually associated with the process. PaaS cloud application development can be used for:
- A database running infrastructure;
- Operating systems;
- Development tools;
- Middleware.
The common PaaS cloud platforms are Windows Azure, OpenShift, and Heroku.
Infrastructure as a Service or IaaS
In IaaS, a cloud service provider manages the entire business infrastructure, including network, data storage, server, and virtualization through an internet connection. The infrastructure can be managed by a public or private cloud. The user has access through an API and manages things like the O/S, applications, data, and middleware. The cloud service vendor is also responsible for repairs, outages, and hardware issues. Along with controlling the resources, the IaaS cloud services model also offers additional services for cloud-based app development like:
- Tracking;
- Detailed invoice;
- Load balancing;
- Log access;
- Backup recovery and replication;
- Clustering;
- Security instruments, such as data encryption protocols and PSI-DSS compliance.
Some popular cloud application development examples that use IaaS cloud services include Zoom, Slack, Vimeo, and PayPal.
Desktop as a Service or DaaS
Desktop as a service is another cloud computing offering in which a service vendor delivers virtual apps and desktops to end users over the internet with a user subscription license. This managed desktop solution is used to provide secure SaaS and legacy applications and full Windows-based virtual desktops. The provider takes care of backend management, which typically includes maintenance, backup, updates, and data storage. Cloud service vendors may also handle security and apps for the desktop, or users may manage these service aspects individually. DaaS offers a pay-as-you-go subscription model, making it easy for businesses of any size to scale up or down on demand.
Cloud Application Examples
Cloud computing services can be used for individual needs or by a company/enterprise. By delivering a range of remote-based applications and services, cloud computing plays a significant role in optimizing business resources and helps in facilitating remote working and remote learning at minimal costs. Below, we have collected real-world examples of cloud computing applications.
| APPLICATION TYPE | EXAMPLES |
|---|---|
| Art | Adobe Creative Cloud, Vistaprint |
| File Storage Platforms | Media Fire, Rapid Share, Hot file |
| Image Editing | Adobe Creative Cloud, Fotor |
| Data Storage | DropBox, Mozy, OneDrive, Box, Google Suites |
| Antivirus | Sophos, Kaspersky |
| Entertainment | Project Atlas, Google Stadia |
| URL Conversion | Bitly |
| Meeting | Zoom, GoTo Meeting |
| Presentation | Slide Rocket |
| Social Media | Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, Facebook |
| GPS | Google maps, Yahoo maps |
| Accounting | Outright, Kash flow, Zoho books |
| E-commerce | Amazon, eBay |
| Management | Evernote |
| Back-up and Recovery | Backblaze, Idrive personal, CrashPlan |
| Cyber Security and Data Governance | Z-Scalar, Carbonite cloud, Forcepoint |
| Big Data Analytics | Apache, Hana, Hadoop |
| Testing and Development | Load storm, SOASTA CloudTest, BlazeMeter |
| Education | Coursera, Canvas, Google Classroom, Blackboard |
Benefits of Using Cloud-Based Applications
The annual growth rate of public cloud services worldwide in 2022 and 2023 by segment

In 2022, 94% of all companies worldwide use cloud computing in their operations. Cloud application development benefits any business as most of the processing issues and data storage are taken care of by remote servers, avoiding the need for physical storage systems. Besides this, cloud software development has various advantages that help businesses achieve their goals.
Cost-Efficiency
Deploying application development in the cloud, you will have quick access to all the information you need and save the resources required to launch an application. Most cloud services are charged as far as they are used, so you don’t have to pay for the unnecessary cloud space or feature set, choosing only the ones you need for your application development model. This pay-as-you-go system applies to all cloud deployment services, providing lower costs and better results.
Data Coherence
With cloud services, your business won’t suffer from inconsistent reporting as cloud-based systems allow entrepreneurs to save all data in a similar location and format. With this data coherence, all the updates will be accessible to every one of the certain cloud spaces, helping them avoid human mistakes and maintain information consistency.
Flexibility
Developing cloud-based apps generally offers more flexibility than hosting on a local server. Also, if you need more bandwidth, cloud services can supply it instantly rather than going through a long sophisticated update to enhance your IT infrastructure. This enhanced flexibility and independence can have a significant impact on the overall capacity of your business.
Wide Geographic Reach
Instead of relying on a single geographic location to host your software, cloud services allow you to host application data centers around the world. Enterprises also use content delivery networks to expand their geographic reach, even if the application is hosted in a single location, which reduces the number of requests made directly to your application and helps to scale it better.
Mobility and Insight
Cloud application platforms allow users to access information across any device, gadget, company, or team to remain updated. According to statistics, organizations investing in cloud services have better employee engagement and satisfaction than local hosting companies. Cloud application development also helps with personalized customer data insights to improve data access speed and experience.
High Scalability
With cloud-based application development, enterprises can use the processing power they need on demand, which is very convenient when a company is expanding and conventional on-premises solutions can’t keep up with the growing workload. The cloud app development will provide you with the required scalability as soon as possible, adjusting to the current business needs. The scalability provided by the cloud enables you to manage a more significant number of customers on a regular basis, resulting in increased profits for your company.
A Varied Range of Solutions
Cloud-based solutions, from CRM to ERP, can significantly contribute to the organization’s success by extending the business model's range of services and resources.
Disaster Recovery
Cloud services also offer a greater redundancy, which plays a critical role in disaster recovery. Without the cloud, companies that want to ensure disaster recovery need to dedicate a separate data center and set up the tools to replicate data or provide backups required for restoring systems, which requires an additional investment. Cloud services can handle this without the need to create infrastructure, allowing you to prepare and set up a disaster recovery environment beforehand that works when you need it.
Easy Deployment
Cloud services offer some unique features that enable teams to handle the deployment much more easily. For example, you can automate certain parts of the deployment process by integrating a source control system into your business. In addition, the deployment slots allow performing no-downtime deployments in a production environment. Once you ensure that everything is working correctly, you can easily swap out production staging slots to go live. Your team can also use the cloud to direct a small percentage of production traffic to staging slots to test the new features in production and ensure everything works correctly before releasing it to the public.
What Are Cloud-Based Applications’ Tech Challenges?
Along with the benefits cloud-based application development provides, it is a technically demanding and challenging process with hidden pitfalls. We’ve prepared some of the most frequently faced challenges to help you understand how to organize cloud application development appropriately for your business.
Service Design
It is critical for cloud applications to be tightly coupled with service logic and implementations in a customer-facing world. Although simple in principle and infrastructure, it can be challenging for cloud application developers to build flexible and reusable components that match the service features.
Security
A large data amount is stored and handled by cloud-based solutions, which makes every business using these technologies vulnerable to cloud security risks. One of the enterprises' primary tasks is ensuring that client data is safe. To improve the security of cloud-based apps, you should use SSL protocols and encryption standards like DES, 3DES, and AES to protect the stored information. You can also use a cryptography approach if the encrypted data is stored in different clouds. If your cloud app provides card payments, you must also care about PCI-DSS compliance to provide cardholders’ data security.
Reliability
If you want your cloud application to run smoothly and without mistakes, it’s recommended to choose a reliable cloud vendor. AWS is considered one of the most reliable cloud frameworks, and its services are frequently used for cloud-based app development. Besides this, you should also monitor cloud service usage, robustness, and productivity and learn SLAs, making sure your apps are available anytime.
Interoperability and Portability
Interoperability is the ability to write code that is well-versed with multiple cloud providers simultaneously, despite the platform differences. However, the burning issue is the communication of different platforms through one code structure. To do this, cloud application developers require strict and standardized work protocols.
Performance
The application’s performance is critical for customer experience. According to Forbes, nearly 70% of consumers say page speed impacts their willingness to buy - the longer a web page takes to load, the higher its bounce rate will be. Global cloud providers offer users the same page loading speed regardless of their location, while it is also common to use CDN to speed up content distribution and improve customer experience.
Scalability
Scalability can also be an issue when developing cloud-based apps, although you can use a hybrid cloud architecture to achieve maximum scalability. A hybrid cloud model can scale up or down if needed, which is highly beneficial when the popularity of your app rises, and you need to handle the extra data flow.
Cloud Apps Development: Steps to Follow
With the cloud, individuals and small businesses can snap their fingers and instantly set up enterprise-class services (Roy Stephan, Founder and CEO, PierceMatrix).
Cloud application development varies from mobile development services to web development, and it’s always better to choose the most appropriate approach that fits your project idea beforehand. It’s also essential to have an investing mindset when working with cloud-based app development and have a good knowledge of your customers. Before you begin, you should identify your target audience, their plans, demands, and pain points, and consider how your product may help them. Below are the main steps you can follow to create a cloud app the right way and compete in the market successfully.
Market and Requirements Analysis
The first step in developing a cloud-based product is analyzing market requirements to understand what apps are suitable for transferring to the cloud and determine the most effective cloud deployment model for your business. You should also pay attention to your business goals and the crucial factors for its functioning, like timeframes, funds, etc. To create a valuable business solution that will be attractive to your core audience and understand the possible pain points, you should conduct market research and evaluate your competitors in the selected domain. You also need to explore feature sets and business models in order to form the product requirements and create a unique and competitive app.
Development Team Hiring
Cloud app development requires an experienced team that will be able to get you quick business model analysis, application development cost estimation, and project planning reports. A reliable and talented cloud app development company will help you to create an application workflow, choose the app’s MVP features, and design the product concept. There are three common options for hiring cloud app developers:
- Cooperate with freelancers. To date, this option is prevalent, although you should note that cloud development necessitates long-term collaboration, while freelance developers can move away for any reason, including the lack of interest in your project.
- Create an in-house team. With an in-house development team, you can manage the whole app creation process, although this is the most costly option. In addition to in-house staff salaries, you should include rent, taxes, hardware, software, and other expenses.
- Find a reliable outsourcing company. This option is gaining popularity due to the high quality of the end output at a lower cost compared to in-house team creation. Hiring a dedicated development team entails benefits like cost-effectiveness, development rapidity, unlimited access to tech talents, comprehensive management, and outstanding flexibility of cooperation.
Architecture and Features
For efficient cloud app development, you need to specify aspects such as service model, application architecture, and cloud migration. All these decisions would impact your product’s performance, so the best choice is to discuss them with the vendor’s experts, who would be able to offer the best alternatives matching your business goals.
- Service model. The choice of a particular model among SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS solutions is required to build an app that would meet your business needs and be able to react to the changes in app users’ requirements.
- Architecture. To date, specialists recommend drawing attention to microservices-based architecture. Cloud solutions are usually monolithic, so all the changes in the app require system rearrangement, which is a complicated and costly process. Microservices architecture's advantages help avoid it and are commonly used for cloud applications.
- Cloud migration. If you’ve already got a running business, it can be optimized with cloud migration by moving the company’s data to the remote cloud server provided by service vendors like AWS or Azure.
It is recommended to consult professionals while selecting tools for cloud-based app development. They will look at your features, design, and needs and determine which tech stack is best for your product. The experts will also build the product’s wireframes and create its specification for you to approve. A typical tech stack for creating simple and advanced cloud-based apps include:
| FOR DATA AND APP | FOR DEVOPS | FOR BUSINESS TOOLS |
|---|---|---|
| ClearDB | DataDog | Jira |
| Akamai | New Relic | G Suite |
| Cloudant | Jenkins | UXPin |
| Bitbucket | DocuSign | |
| Sauce Labs | InVision | |
| Cloud9 IDE | Balsamiq | |
| Puppet Labs | Salesforce Sales Cloud | |
| StillAlive |
Designing the App
When all the tech things are agreed upon, it’s time for the UX/UI design process. The design team will prepare a user-friendly app interface incorporating the best transitions, styles, and animations to make the app feel smooth to use and convenient for navigation. The team analyzes and classifies all the information received from the client and fills in gaps if necessary. If the client has a brand book or a unique corporate style, it’s essential to follow it and ensure it’s well accompanied.
Choosing an App Monetization Model
When you know what your target audience needs, you can predict what your clients will pay for and choose an appropriate app monetization model. There are four models to choose from:
- Paid Model. The model means your app isn’t free to download. If people want to use it, they must first purchase the app from an app store. The key to success with the paid model is your ability to demonstrate the perceived value of your app through screenshots, five-star reviews, etc., that differentiate your app from your competitors.
- In-app purchase. This strategy involves selling physical or virtual goods within your app and retaining profits. In-app purchases can include a wide variety of consumer goods, such as clothes and accessories, although in-app purchases can also be virtual goods, such as extra lives or in-game currency.
- Freemium. The app is offered for free in this business model, although some features are gated and cost money to be unlocked. The goal is to collect and engage app users until they are willing to pay for additional in-app tools.
- Advertising. With this model, you remove the price barrier to purchasing your app and allow free downloads. The primary goal here is to accumulate a large user base and collect information about the people interacting with your app. This data is then sorted and sold to app publishers who pay to place targeted ads in the app.
Developing and Testing the Product
When all the requirements are set and agreed upon, the developers start building the application. Usually, cloud solutions are developed in accordance with Agile/Scrum methodologies, with the building process split into sprints, where one sprint is equal to ten working days. The process begins with the planning stage, in which the team discusses the workload they will deal with. Cloud-based application development is an extremely important step when building such solutions as they offer more customization with simpler processes.
To prevent problems with the cloud app, the development team must test the product before releasing it. At this stage, you must ensure your application works correctly and provides the desired functionality and user experience. Some outsourced development companies offer design, development, and testing services that result in a higher-quality final product. It’s also highly recommended to collaborate with one vendor during the whole process of cloud app development, as only the team capable of imaging the broad picture can customize the product correctly.
App Deployment and Placing in Stores
The final step of the development process is the application deployment and placing it in stores. If the cloud-based application needs to be published on one of the marketplaces, you need to work with Google Play for Android apps or App Store for iOS. Google Play applies automated testing to accelerate the process, although it may be difficult to understand why an application has been rejected in the result. Google Play also doesn’t charge its analogous fee. The App Store delegates application validation to real people. In case there are any bugs, they will demand to perform specific changes for the app approval. For the App Store launch, you’ll need to pay $299 per year to join Apple Developer Enterprise Program.
The placing process includes the following stages:
- Ensure the app follows Google Play or App Store guidelines;
- Fill in the data you want to add;
- Submit the application to review;
- Wait for the reply until the store’s team tests the app to ascertain it works without failure;
- The app will be approved or declined in 2-3 days.
You should also note that application deployment can take some time and require additional modification and development costs.
How Much Does It Cost to Build a Cloud-Based Application?
Cloud-based application development cost usually relies on factors like:
- Application design;
- Application features;
- Location and rate of the outsourced development team;
- Project complexity and size;
- Technology stack;
- Timeframe.
The cost of a cloud-based application consists of:
- Development cost;
- Cloud hosting prices;
- Additional services cost (third-party API).
An approximate structure for developing a SaaS application is shown in the scheme below.

For example, using Brocoders calculator, you can estimate the cost of developing a mobile application and check how many hours a particular function takes. Then, by multiplying this by the rate of developers, you will get the average cost.
For a web application, the table below shows the approximate hours required to develop the basic functions of a SaaS application.
| MAIN SAAS BLOCKS | WHAT CAN BE INCLUDED IN THE BLOCK | TIME REQUIRED, HOURS |
|---|---|---|
| Design | 6-7/page | |
| General Application Set Up | 20 | |
| Authentification | Login and registration block using email | 20 |
| Multi-factor authentication | 5 | |
| SSO | ||
| Social media authentication | 12 | |
| User/Company Entity | User entity | 10 |
| Company entity | 4 | |
| Integration With External APIs | Payment integration (Stripe) | 40 |
| Google Maps and other mapping services integration | 40 | |
| Mailing service integration | 5 | |
| Martech systems integration (CRM, CDP) | 12 | |
| AI integration | Up to 36 (depending on complexity) | |
| Complex custom integration | ||
| Subscription Plans | 3 | |
| Notification | 20 | |
| Admin Panel | 20 | |
| Front-End Development | Dashboard and analytics (charts, tables) | 20 |
| Games, landings, ads constructors | 20+ | |
| Multi-stage visas, challenges (completing assignments and training) | 20+ | |
| Search | 20+ |
On average, the cost of a cloud-based application development ranges from $50,000 to 200,000. Now, let's move on to the additional costs for application development — cloud hosting.
Cloud Hosting Prices
Selecting one cloud vendor over another can be a daunting task as they all offer flexible computing, storage, and networking combined with self-service, instant provisioning, and autoscaling. However, each provider differs in critical areas that may significantly impact your cloud bill. Below, we’ve collected storage and compute pricing across Microsoft Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to check the nuanced differences between these vendors.
Computing often drives up cloud computing bills, but it also provides the best opportunity for cost optimization. We’ll compare virtual machines with the same operating system and within similar regions. The instances we selected for our cloud pricing comparison include the following:
| CLOUD PROVIDER | MICROSOFT AZURE | AWS | GOOGLE CLOUD PLATFORM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Purpose | Compute Optimized | General Purpose | Compute Optimized | General Purpose | Compute Optimized | |
| Instance Type | B4ms | F4s v2 | t4g.xlarge | c6a.xlarge | e2-standard-4 | c2-standard-4 |
| vCPU | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| RAM (GB) | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 16 |
Hourly Pricing Based on On-Demand Rates of Each of These Virtual Machines Across Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud Platform:
| CLOUD PROVIDER | MICROSOFT AZURE | AWS | GOOGLE CLOUD PLATFORM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Purpose | Compute Optimized | General Purpose | Compute Optimized | General Purpose | Compute Optimized | |
| Instance Type | B4ms | F4s v2 | t4g.xlarge | c6a.xlarge | e2-standard-4 | c2-standard-4 |
| vCPU | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| RAM (GB) | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 16 |
| Price | $0.166 | $0.1690 | $0.1344 | $0.153 | $0.150924 | $0.2351 |
Azure is the most expensive choice for general-purpose instances, although it’s one of the most cost-effective alternatives to compute-optimized instances. At the same time, GCP offers the highest price for compute-optimized instances but has double the RAM of alternatives from AWS and Azure.
Discounted Pricing With a One-Year Upfront Commitment:
| CLOUD PROVIDER | MICROSOFT AZURE | AWS | GOOGLE CLOUD PLATFORM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Purpose | Compute Optimized | General Purpose | Compute Optimized | General Purpose | Compute Optimized | |
| Instance Type | B4ms | F4s v2 | t4g.xlarge | c6a.xlarge | e2-standard-4 | c2-standard-4 |
| vCPU | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| RAM (GB) | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 16 |
| Price | $0.0974 | $0.10 | $0.079 | $0.094 | $0.095092 | $0.13156 |
| Discount | 41% | 41% | 41% | 38% | 63% | 63% |
AWS and Azure get a similar discount rate with a 1-year commitment, although AWS offers a cheaper alternative. As for discounts, GCP provides the greatest discount in both general-purpose and compute-optimized instances, but it’s still not the cheapest option.
Average Pricing on Additional Services
SSO Solution Pricing
| PLAN NAME | PRICING FOR 5000 MAU, $ | PRICING FOR 1000 MAU, $ | PLAN FEATURES |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auth0 B2C Professional | 1000 | 240 | Pro MFA; External databases; Admin Roles; 10 Actions, rules, hooks; Consolidated user stories; M2M Add-ons. |
| Auth0 B2B Professional | 1500 | 800 | 3 Enterprise Connection; External databases; 10 Actions, rules, hooks; Admin Roles; 100 Orgs; M2M Add-ons. |
| AWS Cognito | 74 | 14 | For users who sign in through SAML or OIDC federation via enterprise identity providers. Next to 50 MAUs, $0.015 per one. |
| AWS Cognito with advanced security features enabled | 321 | 62 multiplier compliance | Provide risk-based adaptive authentication. Allows you to request additional verification via SMS or a time-based one-time password (TOTP) or block the login request. Protection against the usage of compromised credentials. It prompts users to change their passwords. |
FinTech software is particularly demanding in terms of security, speed, and smooth transactions; therefore, Cognito with advanced security features or the B2B Professional plan with Auth0 is preferred. Based on the price approach, if comparing 5000 MAU, AWS Cognito ($320) is preferable to Auth0 ($1500).
Mailing Services Pricing
| SUBSCRIPTION PLAN | PREMIUM | STANDARD | ESSENTIALS | FREE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price/month, $ | 292,37 | 16,62 | 10,76 | 0 |
| Monthly Email Sends | 150,000 | 6,000 | 5,000 | 2,500 |
| Maximum Contacts | Unlimited | 100,000 | 50,000 | 500 |
| Users | Unlimited | 5 Seats | 3 Seats | 1 Seat |
| Customer Support | Phone & Priority Support | 24/7 Email & Chat Support | 24/7 Email & Chat Support | 24/7 Email & Chat Support |
How Bro Can Help You
Brocoders is a leading tech partner for building web-based and mobile application products. With over 8 years of experience and 60% senior engineers on board, we can help you scale up your product or develop it from scratch. Besides programming, our service includes graphic design, user experience, and project management consultancies.
As part of our app and software development services, Brocoders experts can help you select a cloud model which suits your business needs. Our top specialists deliver world-class cloud solutions for every business requirement, offering cloud consulting, cloud-native development, cloud machine learning, and flexible cloud management services that bring results. With Brocoders, you can bring your products and services closer to their customers by implementing a custom cloud application developed with your business objectives in mind. We know how to do it quickly and cost-effectively for both iOS and Android without compromising quality and usability.
Wrapping Up
Cloud computing adoption is growing every year and keeps gaining momentum. Businesses all over the world recognize cloud computing benefits and see how cloud-based solutions impact their production, security, revenue, and collaboration. By implementing cloud solutions, enterprises can prevent many of the problems faced by organizations using the on-premises infrastructure. Though cloud solutions are challenging in terms of security, architecture, and scalability, they still provide users with more opportunities, allowing businesses to focus on business processes while leaving all the maintenance issues to the provider. Cloud applications are all about tech advancement and exceptional user value and are considered the current and future standard for most new software projects and legacy migrations.
Published at DZone with permission of Anastasiia Komendantova. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

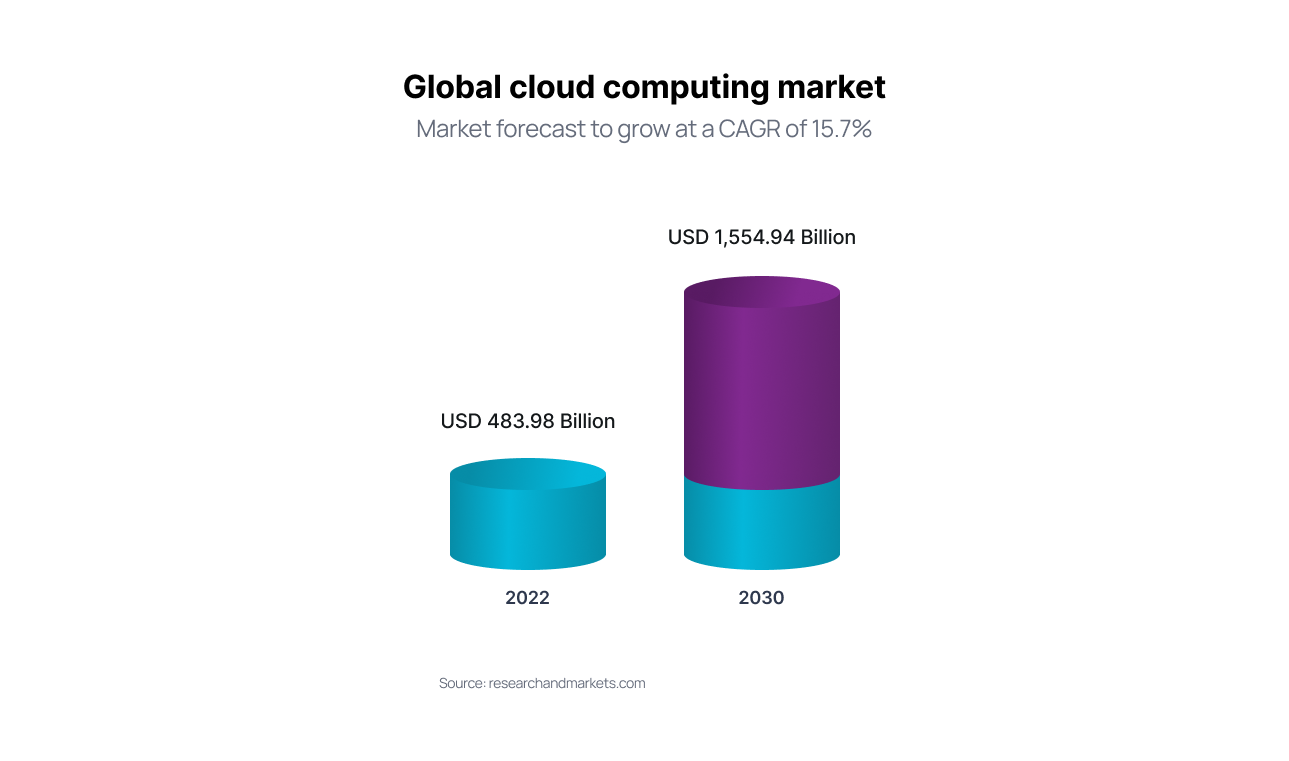 Cloud Applications Prospectives
Cloud Applications Prospectives
Comments