zkEVMs and the Future of Blockchain Scalability
Let’s look at layer 2s on Ethereum—their architecture, why they are needed, what zkEVMs are and how they work, and the details of the new Linea mainnet release.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe hype around blockchain technologies may have quieted, but the builders are still building. The toughest technical problems that kept blockchain from mass adoption over the past few years—slow and expensive transactions—are being solved by layer 2s. zkEVMs, and Linea in particular, are a key part of this solution.
Let’s look at layer 2s on Ethereum—their architecture, why they are needed, what zkEVMs are and how they work, and the details of the new Linea mainnet release.
The Architecture of Layer 2s
Ethereum—the blockchain that first enabled smart contracts and underpins a majority of web3 dApps—has traditionally been slow and expensive. It’s a known problem. Creating a decentralized infrastructure that is fast, secure, and cheap is an incredibly difficult technical challenge. (This is also known as the blockchain trilemma. A network can’t be decentralized and both secure and scalable.)
Let’s look briefly at why.
At a high level, Ethereum has three components:
- The blockchain which keeps track of addresses and their token holdings
- The consensus mechanism where nodes keep track of the movement of tokens among those addresses
- The execution environment where the smart contracts are run (the Ethereum Virtual Machine or EVM)
The Ethereum network prioritizes security over everything else. To ensure the validity of the information in the blockchain, it uses the consensus mechanism to ensure that no one actor by themselves can alter the state of the network. This consensus is an extremely complicated problem that Ethereum (and blockchain) solve.
But in order to solve it, the consensus mechanism was made slow—on purpose. As a result, Ethereum as a whole was slow.
Unfortunately, when you’re trying to build something that needs a modern UX—a decentralized game that stores users’ actions on-chain, or a DeFi solution that manages everything from micropayments to millions of dollars, or a provable way to monetize digital art—it can’t be built on a foundation of slow and expensive transactions.
This is where layer 2s like Linea come in. They are a new generation of blockchains built on top of Ethereum. At a high level, they execute transactions quickly and cheaply using their own novel architectures, then commit those transactions (often as a rolled-up batch of transactions) to the Ethereum blockchain.
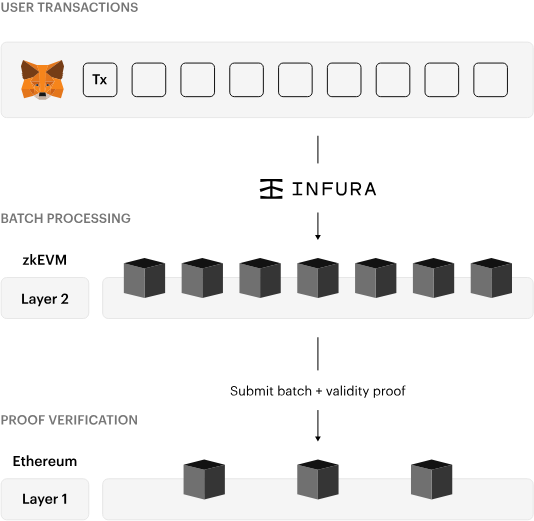
Source: Consensys zkEVM|Consensys
Executing transactions on the L2 minimizes gas fees and makes the transaction fast and cheap. Committing those transactions, in the end, to Ethereum keeps them decentralized and secure. It’s the best of both worlds!
What Are zkEVMs and Why Are They the Future of Blockchain Scalability?
Linea, created by ConsenSys, is a particular type of layer 2 called a zkEVM.
A zkEVM is a layer 2 solution that uses a cryptography technology known as zero-knowledge rollups (ZK rollups). These ZK rollups use zero-knowledge proofs to move those heavy transactions and computations off Ethereum while keeping them secure and easily verifiable.
zkEVMs are especially exciting as L2s because they are EVM-compatible. This means developers can use the existing Ethereum ecosystem—smart contracts, tools, and libraries—they already use with little to no modifications.
Linea goes a step further as a “developer-first” L2, meaning as a primary design developers can bring the tools and processes they already use and know. It’s an L2 that can be used almost identically to the ways developers already use Ethereum.
(For more architecture details see Architecture of Linea.)
Linea: Mainnet Release
Linea was released to mainnet alpha on July 11th, 2023. Linea, and zkEVMs in general, moving to mainnet is perhaps the most critical step needed for mainstream adoption of Ethereum dapps.
With Linea and other L2s, those games and de-fi dapps finally work as they were originally envisioned. They will be fast and cheap enough for the general public. It’s a milestone to celebrate. I encourage you to experiment and try out Linea for yourself. For details on deploying a smart contract to Linea, check out my previous article, Deploy an ERC-721 Smart Contract on Linea.
Before you start, however, let’s cover some of the technical details of the Linea release you should be aware of:
- This is a mainnet alpha release, so there will be initial limitations.
- MetaMask and ConsenSys NFT will be onboarded to mainnet during the first week.
- Over 100 other partners, including Aave, Infura, LayerZero, Truffle, and Uniswap have already integrated with testnet and will move onto mainnet over the coming months.
- Several architectural upgrades are included in this release, including Postman SDK and cross-chain messaging, batch conflation to reduce fixed (verification) costs, and more.
And since this is a mainnet alpha, there are a few key points to remember as you explore:
- The initial release is guarded. ConsenSys is taking measures to ensure the security of the network and user funds, so some functionality might be disabled at first. For one, the network is still somewhat centralized (for now).
- During the first week, RPC calls to the network are only available to partners.
- After that, the network will open to developers.
- There will be initial limits on withdrawals over the first 90 days.
- There is an initial delay with commits from L2 to Ethereum of 8 hours to protect against malicious actors.
- There is not yet full coverage of the EVM opcodes and precompiles.
- Linea does not have its own token; it uses ETH as its native token.
Conclusion
The L2s are here … and Ethereum is finally living up to the hype. Transactions are blazing fast and transaction costs are negligible. And zk rollup solutions such as Linea are leading the way. The next generation of dapps should be fast, cheap, and have superior user experiences. L2s are paving the way to Ethereum scalability and mainstream adoption.
Published at DZone with permission of Michael Bogan. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments