Introduction
History and Vision
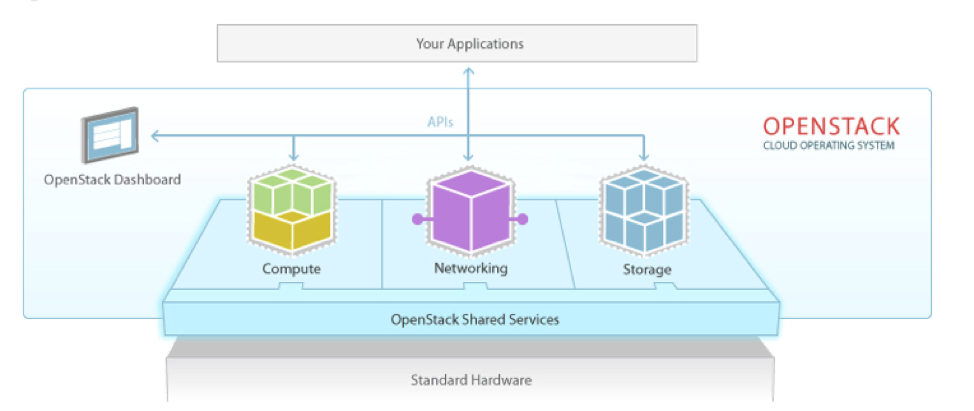
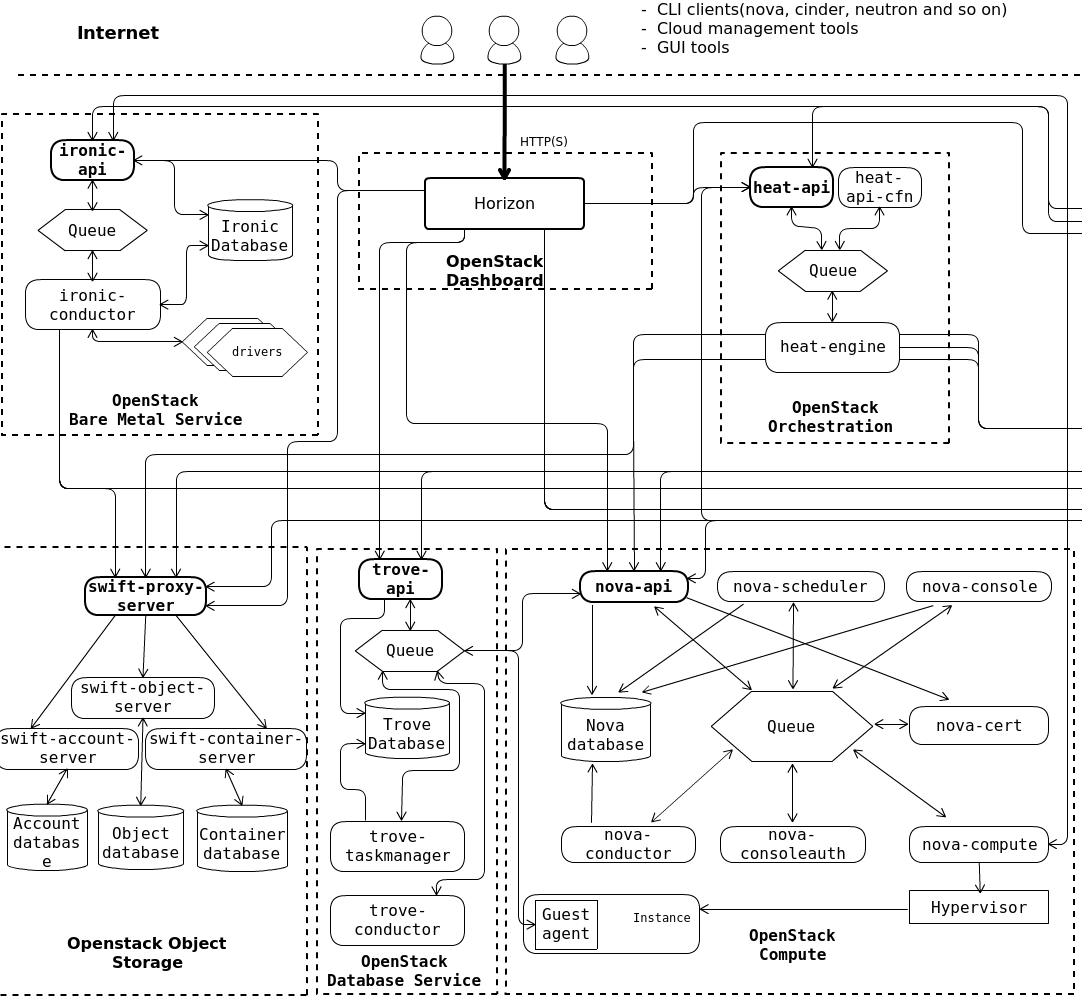
OpenStack is the leading private cloud solution today, with support for numerous infrastructure vendors, multiple distributions, and choice of deployment models, including managed OpenStack, meet your needs. What’s interesting about this mature project is that the code base is completely open source, which means that more developers and operators are continuously examining, optimizing, and fixing software issues beyond what’s available in a traditional software development and support model. Companies actively involved with OpenStack include Platform9, Intel, RackSpace, IBM, and many others.
OpenStack was founded by joint efforts from Rackspace and NASA in 2010. Since its inception, it has grown to support customers such as Walmart, eBay, and Comcast, and has received code contributions from various technology corporations and academic institutions, including Intel and MIT.
OpenStack is one of the fastest growing open source communities in the world, with more than 12,000 member companies and 53,000 individual contributors. It is governed by the OpenStack Foundation, which promotes the development, distribution, and adoption of OpenStack. According to 451 Research, OpenStack-based market revenue was $1.7B in 2016, and expected to reach $2.4B in 2017 and $3.3B by 2018.
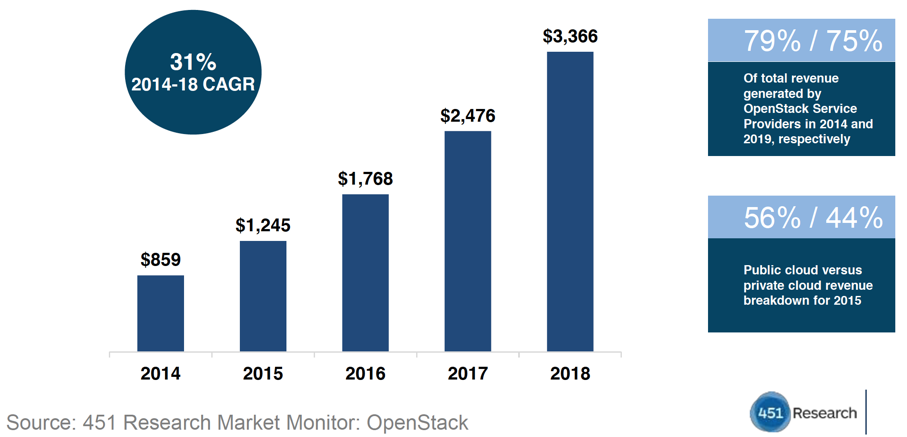
Figure 1: Annual/Expected OpenStack Revenue (Source: 451 OpenStack Pulse 2016)
Adoption Trends
According to another survey commissioned by Suse and conducted by dynamic markets, 96% of businesses are able to identify that there are business advantages of adopting an open source private cloud. Specifically, adopters identify cost, operational efficiency, standardization on open platforms, and no vendor lock-in as their top driving factors for choosing OpenStack. The last factor deserves further elaboration: OpenStack offers a choice of hypervisors that include KVM and VMware ESX, networking options from open source technologies, Cisco, Juniper, VMware, and others, and storage options from NetApp, EMC, Dell, etc. As shown below, OpenStack is used by organizations of all sizes to realize these and other benefits.
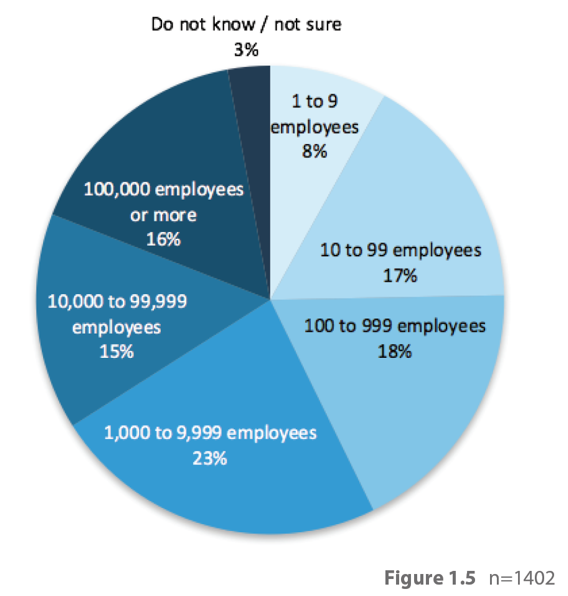
Figure 2: Organization Size Among OpenStack Adopters (OpenStack User Survey, April 2016)
As you may expect, organizations also run different types of workloads on OpenStack clouds such as software development and testing, Continuous Integration and Delivery, infrastructure services, and web services. 21% of OpenStack adopters also report that they are deploying an increasing number of enterprise applications.
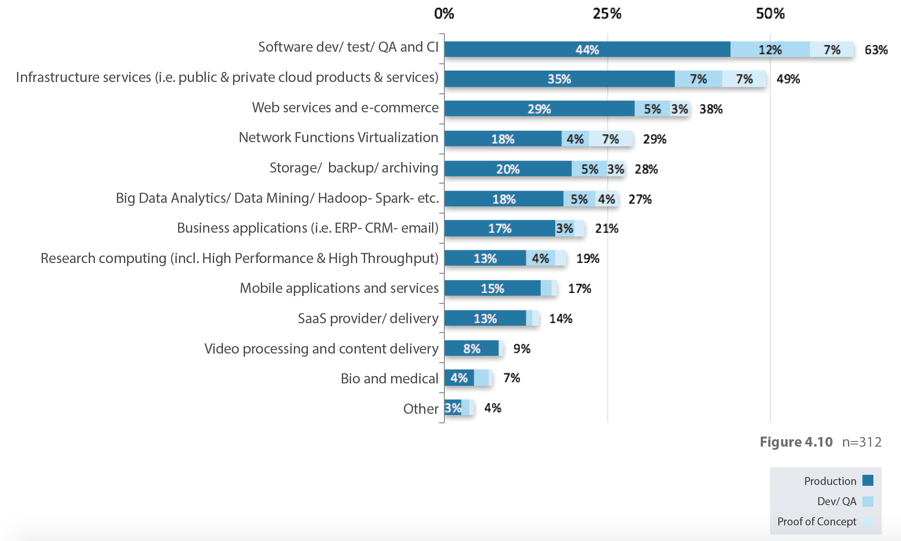
Figure 3: Workloads Deployed On OpenStack Clouds (OpenStack User Survey, April 2016)