All You Need to Know About Asynchronous Messaging and RabbitMQ
This article covers all the basic concepts of asynchronous messaging, it's usability, overview, and key features of RabbitMQ.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this article, I will cover all the basic concepts of Asynchronous messaging, it's usability, overview and the key features of RabbitMQ. In my next post you can read the implementation details and code snippets of RabbitMQ using Java and Spring Boot.
Purpose of Messaging
Messaging provides a mechanism for loosely coupled integration of application components or software, system, and even multiple systems together. It provides a way to communicate loosely, asynchronously, and progressively. There are many protocols that exist that provide this feature, and AMQP is one of the most popular and robust.
AMQP
AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol) is a protocol that RabbitMQ uses for messaging. Although RabbitMQ supports some other protocols, AMQP is most preferable due to compatibility and the large set of features it offers.
RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is a powerful, open-source message broker. It is the most popular and most widely deployed message broker in the world as per it’s official website.
RabbitMQ Installation
Visit RabbitMQ official website where you will find download+install link. Click on this link to go to download and install section. You will get some options for download and install for different OS types. Choose the one suitable for the OS you are using and proceed with downloading and installing.
Note that RabbitMQ also requires Erlang to be installed to make it work. You can find the compatible and recommended version of Erlang for the RabbitMQ version you have installed or selected on this link. Start Installing RabbitMQ and respective erlang one-by-one and choose default options if it prompts you to select.
To verify if RabbitMQ is running or not, you can go to windows services and find the RabbitMQ in the list of services.
RabbitMQ Management UI
After completion of installation, you can visit the RabbitMQ management UI anytime to see the details about exchange, queue, bindings, and messages by opening the management URL in your browser. Default URL is http://localhost:15672 if you have not changed the port number while installing. Default username is guest and password is guest. For more details visit this link.
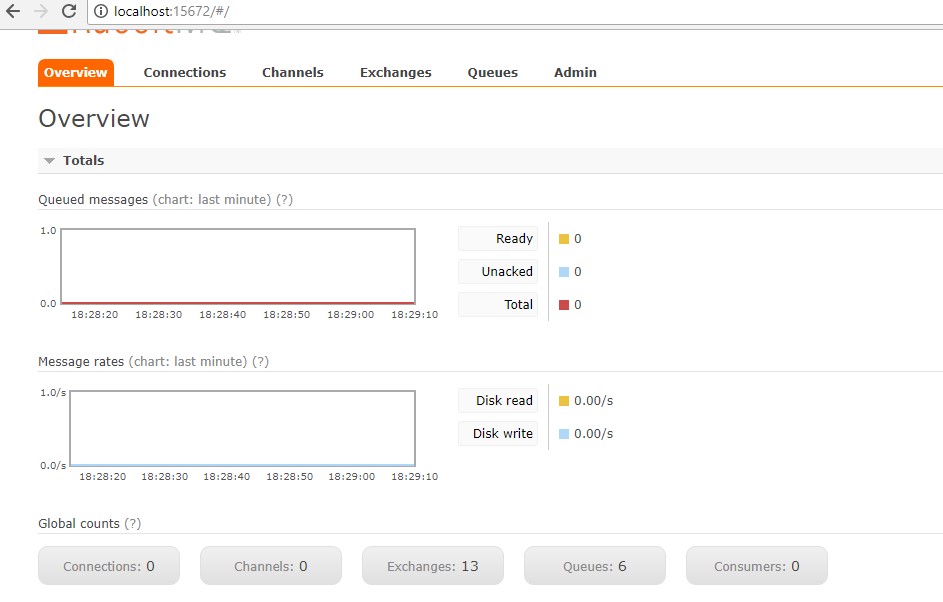
I recommend you play around with various options like sending messages to queue and getting messages from queue in the management UI to get a sense of how it works. Don’t worry if you don’t understand these key terms. In the below sections, I am going to describe these key terms.
RabbitMQ Architectural Design
RabbitMQ Key terms
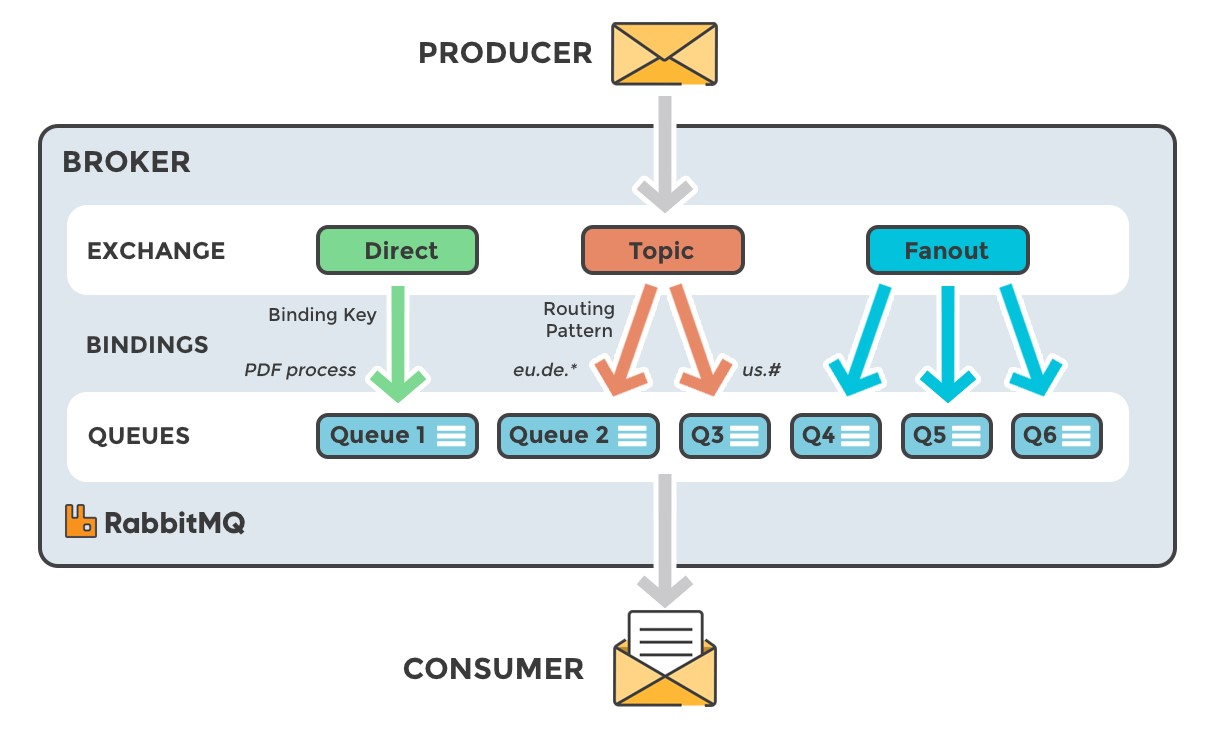
Exchange: Takes a message and routes it to one or more queues. Routing algorithms decides where to send the message from the exchange. Routing algorithms depends on the exchange type and rules called “bindings.”
Exchange Type |
Routing Algorithms |
Purpose |
Direct |
It routes messages with a routing key equal to the routing key declared by the binding queue |
This is a Default exchange type. |
Fanout |
It routes messages to all the queues from the bound exchange. If routing key is provided then it will be ignored |
Useful for broadcast feature using publish subscribe pattern |
Topic |
It routes messages to queues based on either full or a portion of routing key matches |
Useful for broadcast to specific queues based on some criteria |
Headers |
Routes messages based upon matching of the message header to specified header based on binding queue |
Useful for directing messages which may contain a subset of known criteria |
Topics: Topics are the subject part of the messages. These are the optional parameters for message exchange.
Bindings: "Bindings" is the glue that holds exchanges and queues together. These are the rules for routing algorithms.
Queue: Queue is a container for messages. It is only bound by the host’s memory and disk limit. Queues are the final destination for messages before being popped up by subscribers.
Property Name |
Description |
Name |
Name of the queue |
Durable |
Either persists the queue to the disk or not |
Exclusive |
Delete the queue if not used anymore |
Auto-Delete |
Delete the queue if consumer unsubscribes |
Producer: Producer is a program that sends message to a queue.
Consumer: A consumer is a program which receives messages from the queue.
RabbitMQ Configuration
RabbitMQ configurations can be fed using rabbitmq.conf file. The default file location depends on the OS. The default location of the config file on windows is %APPDATA%\RabbitMQ\
To override the main RabbitMQ config file location, you can use the RABBITMQ_CONFIG_FILE environment variable. Configuration details can be found here.
Conclusion
I hope this covers the basic concepts of asynchronous messaging with RabbitMQ and how to get started with it. In my next article, you can find the implementation details including source code on how to integrate a Java, Spring Boot application to RabbitMQ message broker to provide asynchronous messaging features.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments