Ansible Event-Driven Automation for Real-Time Operations
Event-driven Ansible automation uses events to trigger predefined actions, enhancing operational efficiency, ensuring compliance, and minimizing manual efforts.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeEvent-driven automation allows the service team to execute predefined actions automatically in response to specific events within a systems landscape. This approach improves operational efficiency by minimizing manual intervention and allowing systems to adapt quickly to changing conditions. Ansible, a popular open-source automation tool, incorporates event-driven features to support such dynamic and responsive automation.
Key Components of Event-Driven Ansible
Event-driven Ansible automation consists of three main components:
- Event Sources
- Ansible Rulebooks
- Actions
Event sources are the origins of automation triggers, such as webhooks, message queues, or monitoring systems, with the flexibility to integrate custom plugins for specific tools.
Ansible Rulebooks act as a conditional framework, employing "if-this-then-that" logic to automate tasks based on defined event conditions. Actions are the tasks carried out when these conditions are met, which may include executing playbooks, running modules, or invoking external scripts.
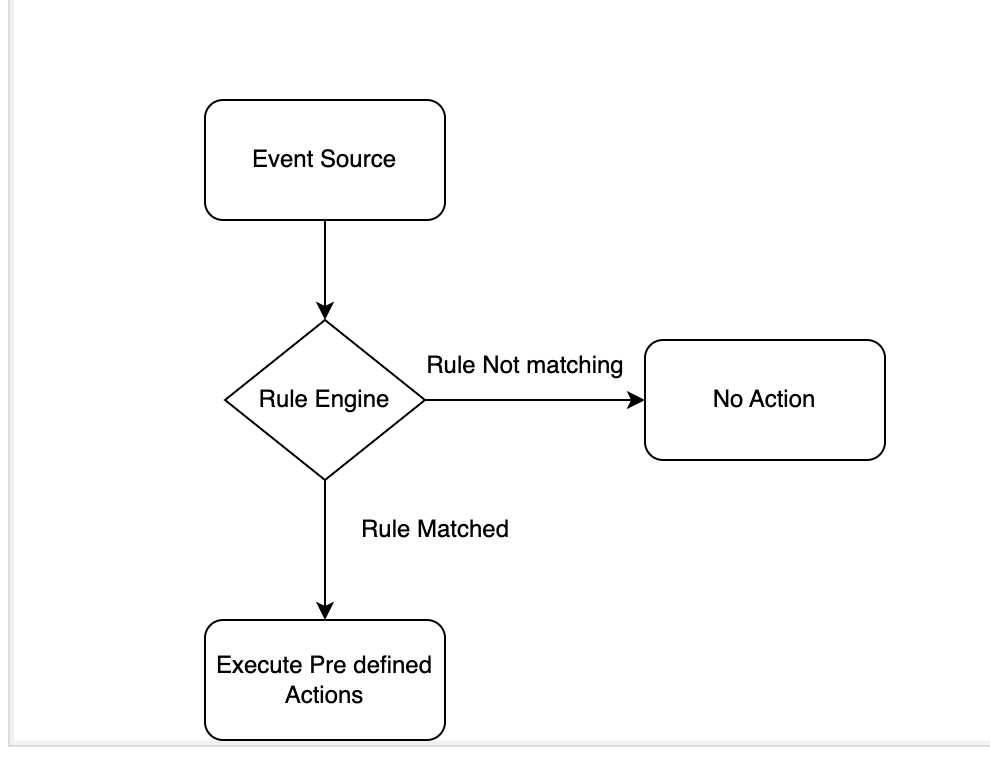
Simple Demo of Event-Driven Ansible
Here is a sample rulebook demonstration to monitor a file for changes using the ansible.eda.file_watch module. It prints the output to the console whenever the file is modified (condition: event.change == "modified").
filewatch.yml
---
- name: Check if the error file is modified recently or not
hosts: localhost
sources:
- name: file_watch
ansible.eda.file_watch:
path: /tmp/errorfile
recursive: true
rules:
- name: Run the action if the /tmp/errorfile is modified
condition: event.change == "modified"
action:
run_playbook:
name: print-debug-msg.ymlprint-debug-msg.yml
---
- name: Playbook for printing the content of the /tmp/errorfile
hosts: localhost
connection: local
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: Cat the content of the /tmp/errorfile and store it in errorfile_output
command: cat errorfile chdir=/tmp
register: errorfile_output
- name: Print the content in console
debug:
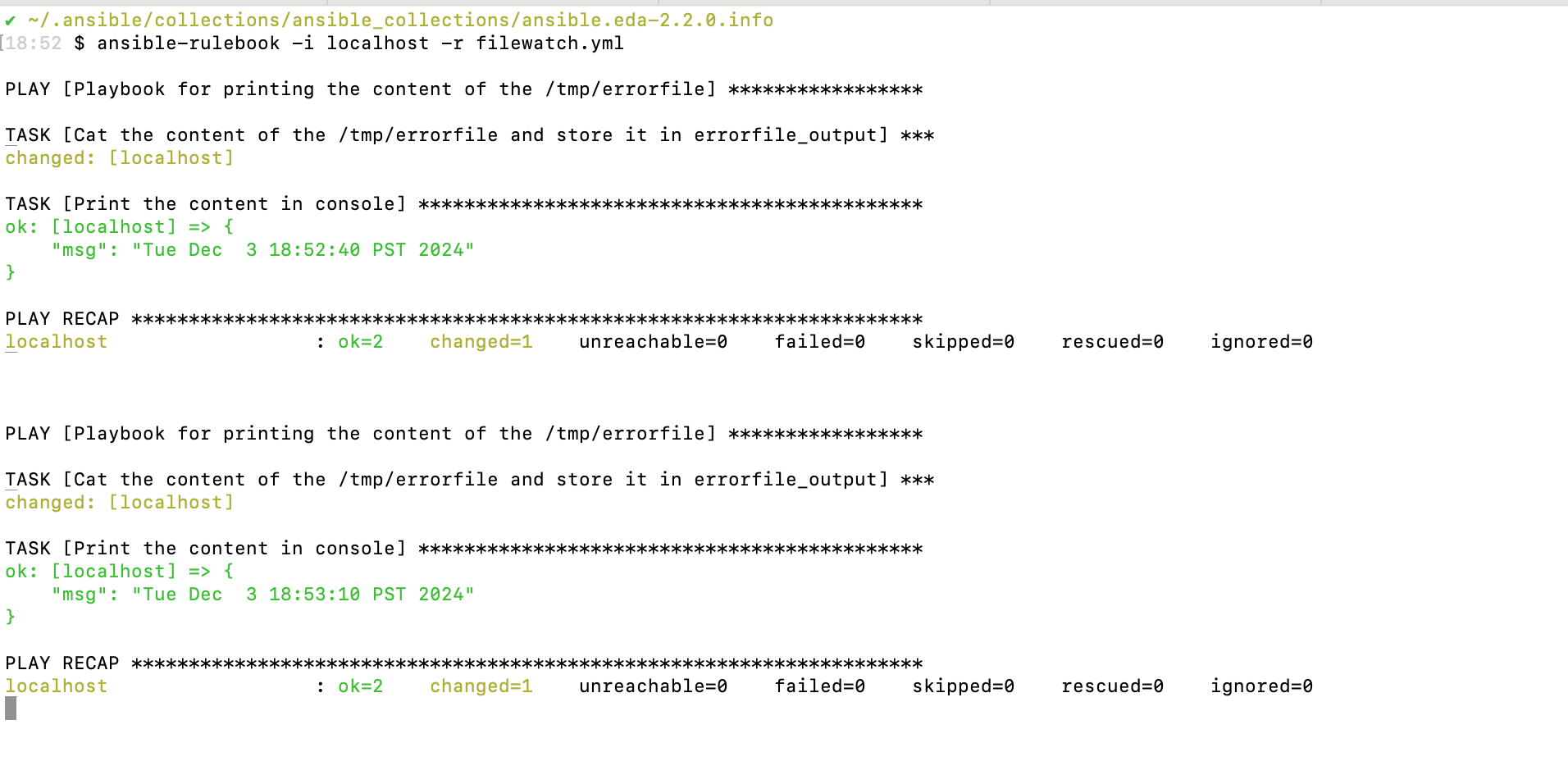
msg: "{{errorfile_output.stdout}}"Executing the command date > /tmp/errorfile to update the file /tmp/errorfile:

Screenshot of filewatch.yml command ansible-rulebook -i localhost -r filewatch.yml:
Key Use Cases
Event-driven Ansible can be applied in scenarios such as automated remediation, infrastructure scaling, and security compliance. Automatically resolving incidents, such as restarting services or scaling resources based on performance thresholds, helps service teams maintain system stability. By dynamically scaling infrastructure or adjusting resources according to demand, teams can optimize performance during peak usage and reduce costs during low-demand periods.
Furthermore, security compliance is ensured by detecting non-compliant configurations and applying corrective measures automatically, adhering to established policies without requiring manual intervention.
Ultimately, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, enabling IT teams to dedicate more time to strategic initiatives. It also enhances responsiveness, as systems can react to events in real time, reducing downtime and improving the user experience.
Additionally, it boosts consistency and compliance by leveraging automated actions that ensure uniform responses to events while adhering to established policies and ensuring comprehensive documentation of environments and actions through automation rulebooks and playbooks, aligning with the Ops-As-Code model.
Conclusion
Event-driven Ansible expands traditional automation by empowering systems to autonomously respond to events, improving operational efficiency while making IT system environments more resilient and adaptable to changing conditions. With Ansible's automation framework, organizations can tailor event-driven automation to address their specific operational needs effectively.
Note: The views expressed on this blog are my own and do not necessarily reflect the views of Oracle.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments