Deep Dive Into Spark Cluster Management
Learn about the different cluster management modes that you can run in your Spark application - standalone, Mesos, Yarn, and Kubernetes - and how to manage them.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis blog aims to dig into the different cluster management modes in which you can run your Spark application.
Spark applications run as independent sets of processes on a cluster, coordinated by the SparkContext object in your main program, which is called the Driver Program. Specifically, to run on a cluster, SparkContext can connect to several types of Cluster Managers, which allocate resources across applications. Once the connection is established, Spark acquires executors on the nodes in the cluster to run its processes, does some computations, and stores data for your application. Next, it sends your application code (defined by JAR or Python files passed to SparkContext) to the executors. Finally, SparkContext sends tasks to the executors to run.
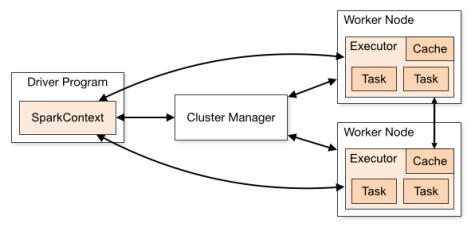
Spark offers these types of cluster managers:
Standalone
Mesos
Yarn
Kubernetes (experimental)
In addition to the above, there is experimental support for Kubernetes. Kubernetes is an open-source platform for providing container-centric infrastructure.
Standalone Mode
It is the easiest of all in terms of setup and provides almost all the same features as the other cluster managers if you are only running Spark. If you would like to run Spark along with other applications or would like to use richer resource scheduling capabilities (i.e. queues, etc.), both YARN and Mesos provide these features. Of these two, YARN is most likely to be preinstalled in many of the Hadoop distributions.
The Spark standalone mode requires each application to run an executor on every node in the cluster, whereas with YARN, you can configure the number of executors for the Spark application.
Mesos Mode
Mesos consists of a master daemon that manages the agent daemons that are running on each cluster node. Mesos framework is responsible for running the tasks on these agents. The master enables fine-grained sharing of resources (CPU, RAM, …) across frameworks by giving them resource offers. The master decides how many resources to offer to each framework according to a given organizational policy, such as fair sharing or strict priority.

A framework running on top of Mesos consists of two components:
A scheduler that registers with the master to be offered resources
An executor process that is launched on agent nodes to run the framework’s tasks
Agent nodes report to master about free resources available to them. The master determines how many resources are offered to each framework and the frameworks’ schedulers select which of the offered resources to be utilized. When a framework accepts the offered resources, it passes a description of the tasks it wants to run on them to Mesos. In turn, Mesos launches the tasks on the corresponding agents.

Yarn Mode
Spark with Yarn can be deployed in two modes.
Cluster Deployment Mode
In this mode, SparkDriver runs in the Application Master on Cluster host.
A single process in a YARN container is responsible for both driving the application and requesting resources from YARN.
The client that launches the application does not need to run for the lifetime of the application.
Cluster mode is not well-suited for using Spark interactively. Spark applications that require user input, such as spark-shell and pyspark, require the Spark driver to run inside the client process that initiates the Spark application.

Client Deployment Mode
In client mode, the Spark driver runs on the host where the job is submitted.
The ApplicationMaster is responsible only for requesting executor containers from YARN. After the containers start, the client communicates with the containers to schedule work.
It supports spark-shell, as the driver runs at the client side.

After going through the details about the three Cluster Managers, now we should understand the use case scenario where one should use which cluster management mode.
To understand that, let's look at their design priorities and how they approach scheduling work.
Standalone is good for small Spark clusters, but it is not good for bigger clusters (there is an overhead of running Spark daemons — master + slave — in cluster nodes). These daemons require dedicated resources. So standalone is not recommended for bigger production clusters.
YARN was created out of the necessity to scale Hadoop. Prior to YARN, resource management was embedded in Hadoop MapReduce V1 and it had to be removed in order to help MapReduce scale. The MapReduce 1 JobTracker wouldn’t practically scale beyond a couple thousand machines. The creation of YARN was essential to the next iteration of Hadoop’s lifecycle, primarily around scaling, whereas Mesos was built to be a scalable global resource manager for the entire data center.
Mesos determines which resources are available, and it makes offers back to an application scheduler (the application scheduler and its executor is called a “framework”). Those offers can be accepted or rejected by the framework. This model is considered a non-monolithic model because it is a “two-level” scheduler where scheduling algorithms are pluggable. Whereas when a job request comes into the YARN resource manager, YARN evaluates all the resources available and it places the job. It’s the one making the decision of where jobs should go; thus, it is modeled in a monolithic way.
When you evaluate how to manage your data center as a whole, you’ve got Mesos on one side that can manage all the resources in your data center, and on the other, you have YARN, which can safely manage Hadoop jobs but is not capable of managing your entire data center.
The language used to develop Apache Mesos is C++ because it is good for time-sensitive work, whereas Yarn is written in Java.
Published at DZone with permission of Sangeeta Gulia, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments