Exploring Deployment Options in Mule 4
Learn about different Mule 4 deployment options, such as CloudHub, Hybrid, and Anypoint Runtime Fabric, for deploying applications in cloud or on-prem environments.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the real integration world, a platform should serve as a bridge between users and developers so that users can access the applications developed by developers. This mechanism of bringing APIs to customers or clients is called API deployment. In technical terms, deployment refers to delivering applications and modules and adding or updating software within an organization.
Now, let's talk about the different deployment options used in Mule 4.
How Do We Deploy in Mule 4?
When we create Mule applications using Anypoint Studio, we must deploy them using one of the deployment options supported by Anypoint Runtime Manager, as the server is not designed for production deployment. We have many ways to deploy our applications:
1. CloudHub
CloudHub is a built-in integration platform as a service (iPaaS) in MuleSoft that provides servers to deploy applications. It is a cloud platform that scales on demand, which allows us to start small and expand as needed. Using Anypoint Studio, applications can be easily deployed to CloudHub.
We can deploy in CloudHub using Anypoint Runtime Manager, Anypoint Studio, Anypoint Code Builder, and so on.
Note: Integration Platform as a service is a cloud-based platform that allows organizations to build integrations between applications, whether in the cloud or on-premises.
2. CloudHub 2.0
CloudHub 2.0 is the latest version of CloudHub, and it offers improved manageability and functioning as a containerized integration platform as a service (iPaaS). It also scales up or down based on client requirements and ensures flexibility in the applications. It is highly secure, protecting sensitive data and services with secret codes. Additionally, it provides an isolation boundary by running each instance in a separate container.
The image below shows the CloudHub 2.0 Architecture that is used in Mulesoft.

3. Hybrid Deployments
Hybrid deployment is a centralized, private deployment model powered by Mule Runtime Servers. It deploys applications from the cloud to Mule servers and leverages Runtime Manager for management. This approach enables seamless movement of applications between cloud and local environments, allowing the same APIs to run on multiple platforms. It ensures high scalability and security.
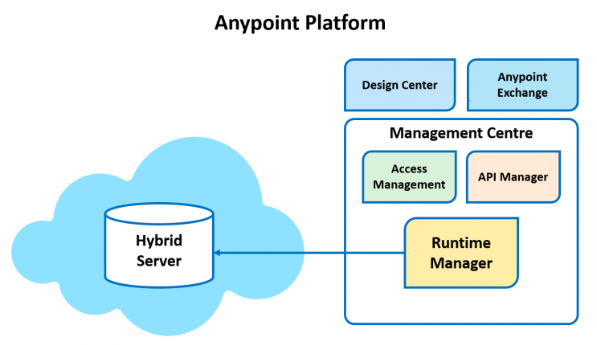
4. Anypoint Platform Private Cloud Edition
In Anypoint Platform Private Cloud Edition, Mule applications can be run and managed directly on a local server without relying on external system connections or internet connectivity. This provides control over data storage, processing, and transfer within the local environment. Customers can manage both the management plane and runtime plane together.
This edition is most compatible with Mule Runtime Engine versions 4.3 to 4.6, improving performance as the versions advance.
5. Anypoint Runtime Fabric
This Anypoint Runtime Fabric automates the deployment and orchestration of Mule applications and the API gateway. It runs on customer-managed infrastructure like AWS, Azure, and virtual machines (VMs).
Conclusion
In this article, we explored various techniques for deploying a Mule application in the cloud or on-premises. It is essential to choose the right platform based on your specific requirements. By choosing the right deployment method, organizations can optimize performance, scalability, and security to meet their business goals.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments