Understanding Why Secrets Like API Keys Inside Git Are Such a Problem
Secrets in version control systems (VCS) like git is the current state of the world despite widely being recognized as a bad practice. But why then are secrets in git repositories so common?
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeTable of Contents
- Why Secrets End up In Git
- Why Secrets in Git Are Dangerous
- Real-World Examples: Recent Data Breaches
- Detecting Secrets in Reviews (or Not)
- Using Automated Secrets Detection in Git
- Wrap Up
Why Secrets End up In Git
A seasoned developer may be scratching their heads wondering why anyone may put secrets inside a git repository. But the fact is, secrets inside git repositories is the current state of the world.
Previously we have discussed why it is common to choose the path of least resistance when it comes to accessing and distributing secrets. Git acts as the central point of truth for a project, so it makes sense, at least from a convenience point of view, that secrets are stored inside a private git repository to make distribution and access easy.
But storing secrets like this is playing with fire, it only takes a very small incident to get burnt.
In addition to intentionally storing secrets in git, when secrets are not managed properly, it is very easy to lose track of them. Secrets may be hardcoded into source code, stored as text file, shared over slack or buried inside a debug application log. in addition, developers can be in large distributed teams with access to a plethora of secrets while being faced with reduced release cycles and an ever-growing number of technologies to master.
Why Secrets in Git Are Dangerous
Source code, we have to remember, is very leaky. Code is copied and transferred everywhere. Git is designed in a way that allows, even promotes, code to be freely distributed.
Projects can be cloned onto multiple machines, forked into new projects, distributed to customers, made public so on and so forth. Each time it’s duplicated on git, the entire history of that project is also duplicated.
Why storing secrets in public repositories is bad will be obvious. They are freely available to everyone on the internet and it is very easy to monitor public repositories, git hub has a public api to fetch all public commits for example.
But What About Private Git Repositories?
Private repositories don’t publish your source code to the internet openly, but it doesn’t have adequate protection to store such sensitive information either. Imagine if there was a plain text file with all your credit card numbers within it; you hopefully wouldn’t put this into the companies git repository, secrets are just as sensitive.
A few things to consider when storing secrets in private repositories:
- Everyone in the organization with access to the repo has access to the secrets within (one compromised account can provide an attacker access to a trove of secrets).
- Repositories can be cloned onto multiple machines or forked into new projects.
- Private repositories can be made public which can have secrets buried in the git history.
Another important consideration is that Code removed from a git repository is never actually gone.
Git keeps track of all changes that are made. Code that is removed - or more technically correct: code that is committed over - still exists within the git history.
Interestingly enough, code is removed from a project at near equal volume that is added. This means that the code within repositories are much deeper than the first layer and secrets could be buried deep within the git history under a mass of commits that have been long forgotten.
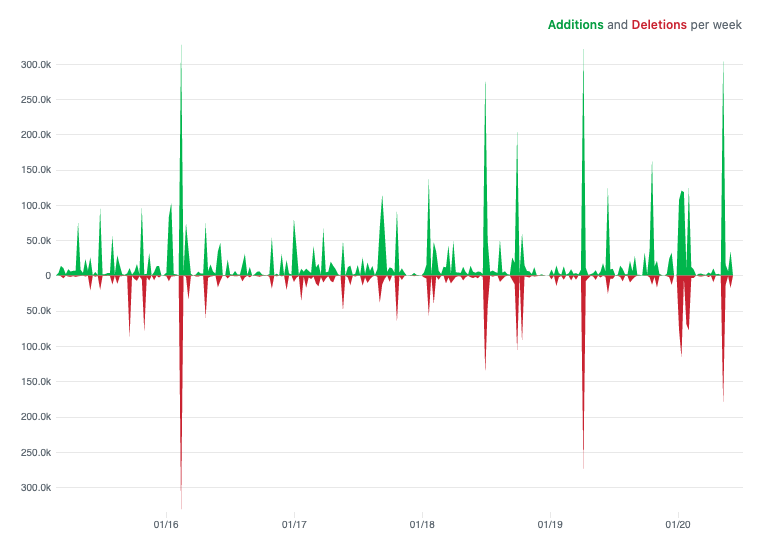
Https://github.com/hashicorp/vault/graphs/code-frequency
Comment: the contributions graph that you see above from hashi corp vault repository is a typical view of a project's history. The regularity you find in project contribution graphs is both surprising and interesting (check out some projects graphs, it seems to be a rule of nature).
Real-World Examples: Recent Data Breaches
Secrets being leaked into public places happens with surprising regularity.
If you perform a search on git hub for the commit message ‘removed aws key’, you will find thousands of results. And that's just within public repositories.
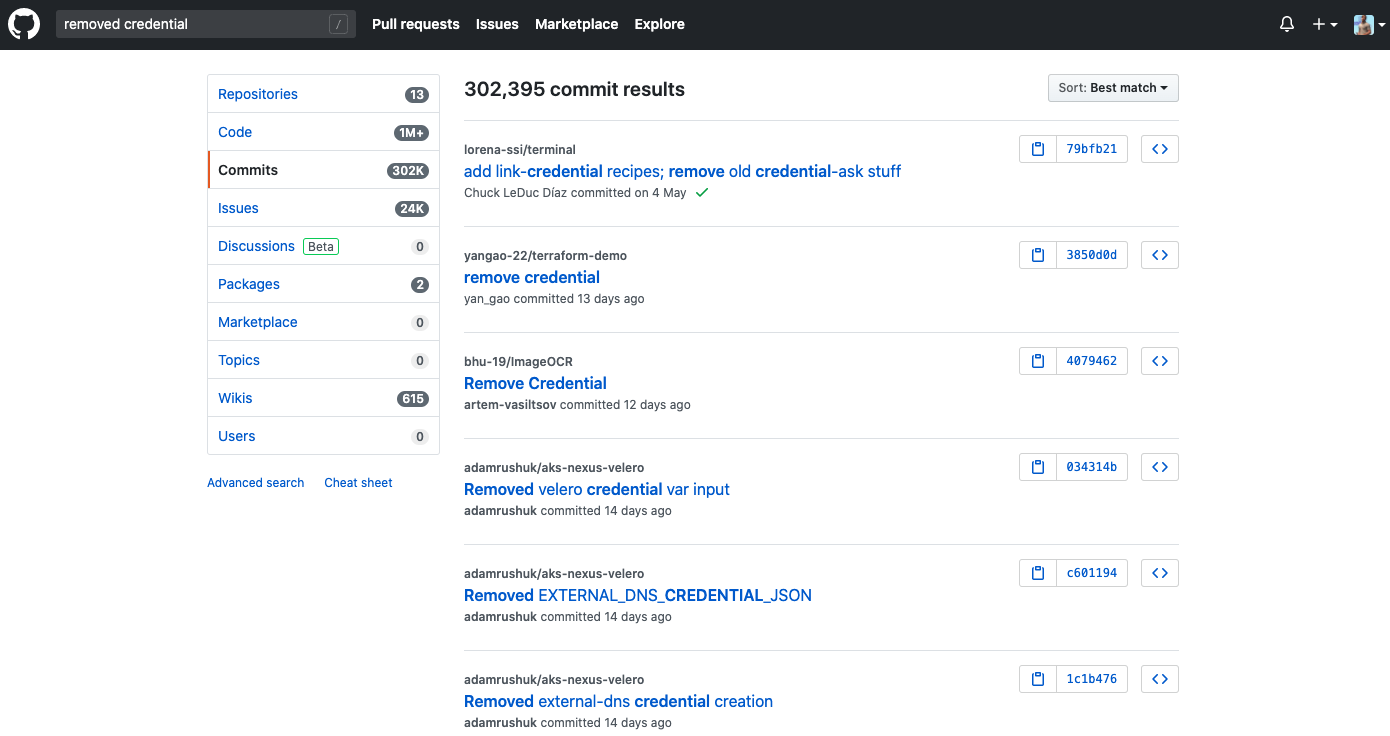
Https://github.com/search?Q=removed+aws+key&type=commits
Git guardian detects over 3,000 leaked secrets each day within public git hub alone, there are thousands of examples for this but below are a couple recent or noteworthy examples.
Publicly Disclosed Examples of Recent Data Breaches Through Leaked Credentials.
- Starbucks Data Breach - January 2020: Jump Cloud Api Key Found in Git Hub Repository
- Equifax Data Breach - April 2020: Leaked Secrets in Personal Git Hub Account Granted Access to Sensitive Data for Equifax Customers
- Uber Data Breach - October 2016: Poor password hygiene allowed intruders to access Uber’s Amazon S3 Datastore using an AWS access key posted in a private GitHub repository.
If this seems like an issue for only large companies to worry about, it’s not. Attackers are constantly exploiting personal services through secret keys too. In one example, bad actors scanned GitHub for AWS keys and used them to mine cryptocurrency, leaving developers with thousands of dollars in debt.
Detecting Secrets in Reviews (or Not)
One great advantage of git is to be able to quickly and clearly see changes made and compare previous and proposed code states. It’s therefore common to believe that if secrets are leaked in source code, they of course will be detected within a code review or in a pull request.
Code reviews are great for detecting logic flaws, maintaining good coding practices and keeping code quality high. But they are not adequate protection for detecting secrets.
This is because reviews generally only consider the net difference between the current and proposed state. Not the entire history of a branch. Branches are commonly cleaned before being merged into the master branch, temporary code is added then deleted, unnecessary files added then removed. But now these files, which are high-risk candidates for containing secrets, are not visible to the reviewer (unless they want to go through the entire history of a branch).
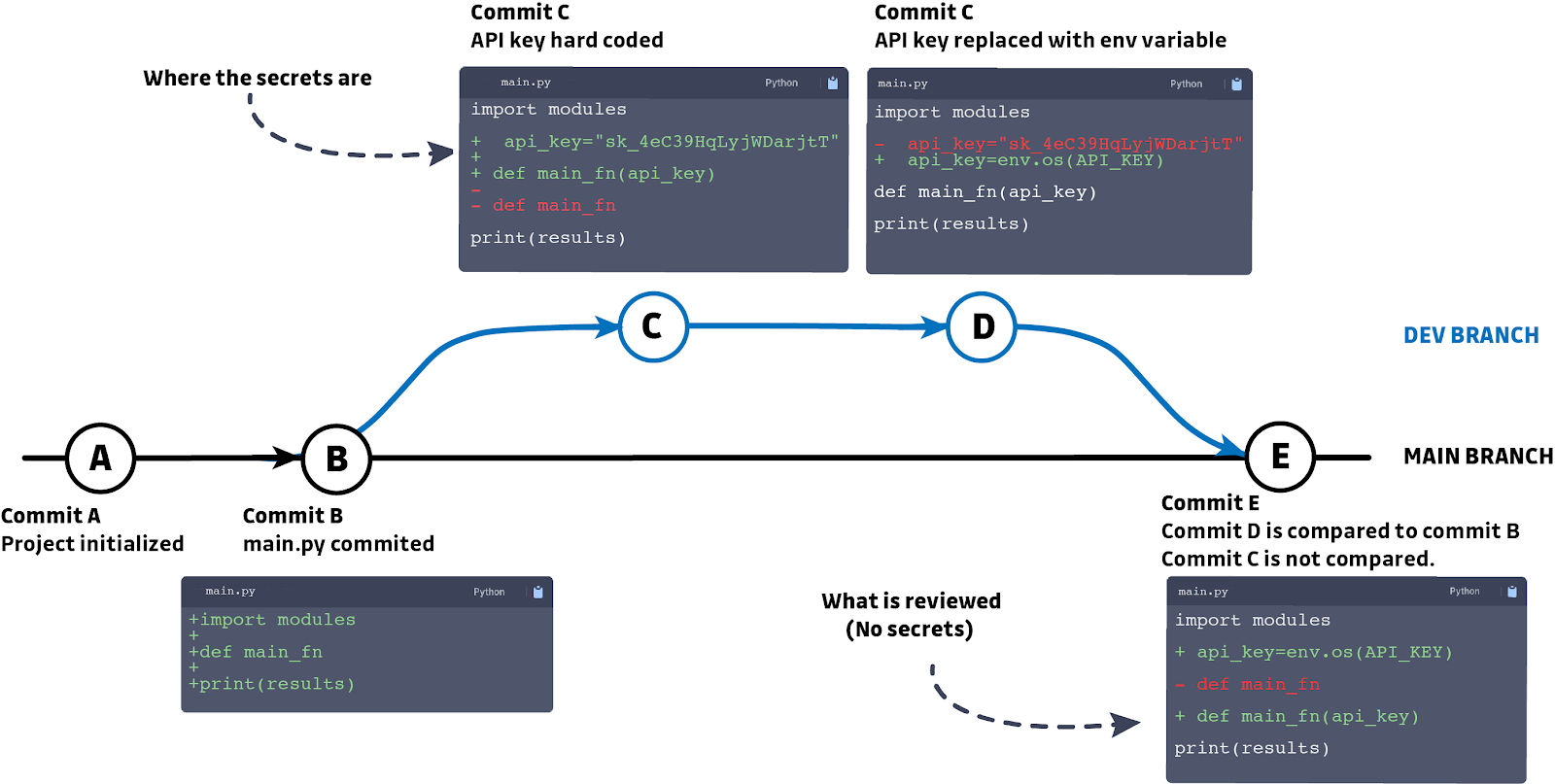 Let's walk through the example above. While this is oversimplified it tells a familiar story.
Let's walk through the example above. While this is oversimplified it tells a familiar story.
Commit B a file named main.py is added. A new branch is created to add a new function to main.py in commit C, this feature uses an API key so to save time for testing this is hardcoded. Once the feature is working the hardcoded API key is replaced with an env variable and the file is cleaned. Finally, a pull request is made and accepted because the reviewer looks at the net difference between commit B and D, ignoring commit C. Now undetected secrets are buried in the git history of the project.
While this scenario is very basic, add in hundreds of commits and files between master and a development branch and you can see how easy it is to miss secrets in code reviews.
Using Automated Detection to Find Secrets in Git
Taking into consideration all we have just discussed secrets inside git, it is clear that this is a problem that will persist and one we cannot solve with human code reviews. While automation is not always the answer, detecting secrets, in particular secrets inside git, automated secrets detection is a clear solution to this widespread problem.
Unfortunately detecting secrets in git is not quite as easy as it first seems because of the probabilistic nature of secrets. This makes it hard to distinguish between a true secret and other random-looking strings like database IDs or other hashes.
The good news, however, is that GitGuardian has built powerful tools for developers to detect secrets in git. A great dashboard with native GitHub and GitLab integrations, a CLI tool called GG-Shield or you can even build custom your own git secrets scanner using the GitGuardian API.
Wrap up
Let’s have a quick review of what we have gone through. Git repositories are very common places to find secrets and they remain the perfect incubator for secrets to sprawl into multiple locations. Git keeps a track of a project's history which can be deep making finding secrets difficult. Because of the workflow git creates, it is common for any secrets to be missed during manual checking procedures and automated secrets detection should be introduced into the SDLC.
Published at DZone with permission of Mackenzie Jackson. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments