Install Anypoint Flex Gateway on the Kubernetes as an Ingress Controller in Connected Mode - Part 2
In part two of the series, learn more on how to install Anypoint Flex Gateway on Kubernetes as an Ingress Controller.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn my last blog, we saw how to set up Flex Gateway on Minikube as an Ingress controller in the Connected Mode and here we will see how to publish the APIs to Flex Gateway.
As we have seen for installing the Flex Gateway, we have used the Runtime Manager and for publishing the APIs, we will be using the API Manager. To achieve this, we have to make sure that Flex Gateway is connected. With Flex Gateway, Anypoint API Manager capabilities can be extended to the MuleSoft APIs as well as to Non-MuleSoft APIs.
Publish the APIs to the Flex Gateway
To Publish the APIs to Flex Gateway, Navigate to the API Manager ⇒ Add API ⇒ Add new API. Select the Runtime as a Flex Gateway and it will list down all the Flex Gateway available in your environment and allow you to publish APIs on those Flex Gateway that is Connected.
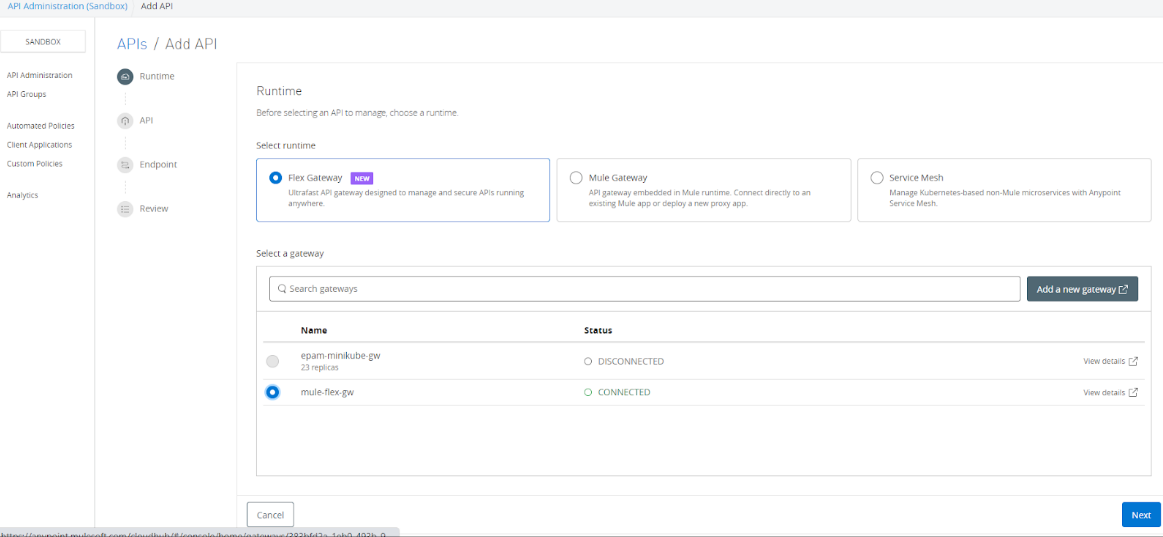
In this case, we will be selecting “mule-flex-gw” and click “Next”. Now, we can Select API from Exchange or Create a new API. In this case, we will be selecting Create new API and provide a few details like Name and select Asset types as an HTTP API and clicking Next.
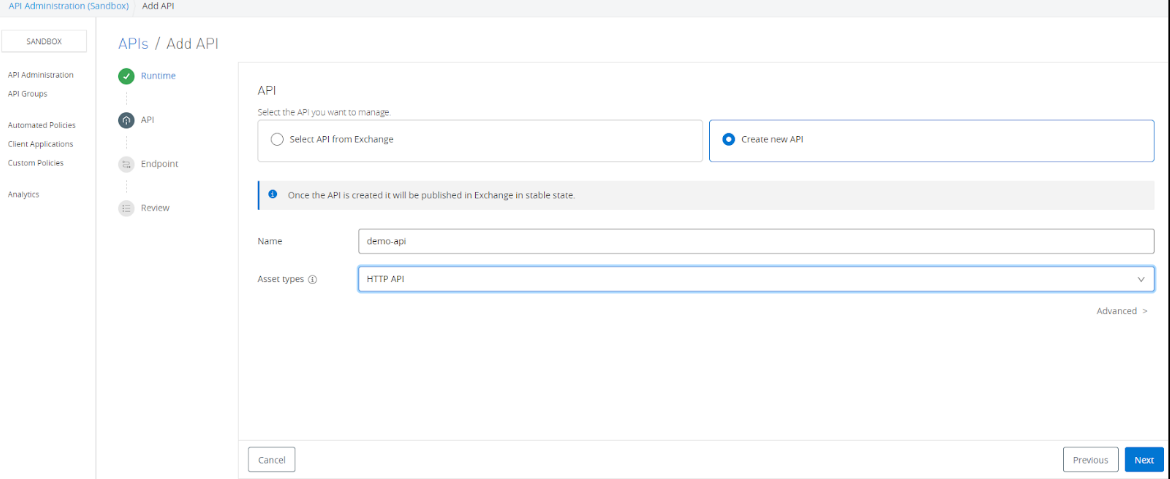
After clicking the Next, it will open a new window, and there few important details that need to provide like Implementation URI (i.e. Url of our API implementation) and in the Advanced options, provide the port number 80 and will be using HTTP protocol.
Note - Make sure the Implementation URL must be accessible from Minikube where we have installed Flex Gateway. We need to take care of appropriate firewall rules and ensure that there is connectivity to implementation URLs from Minikube.

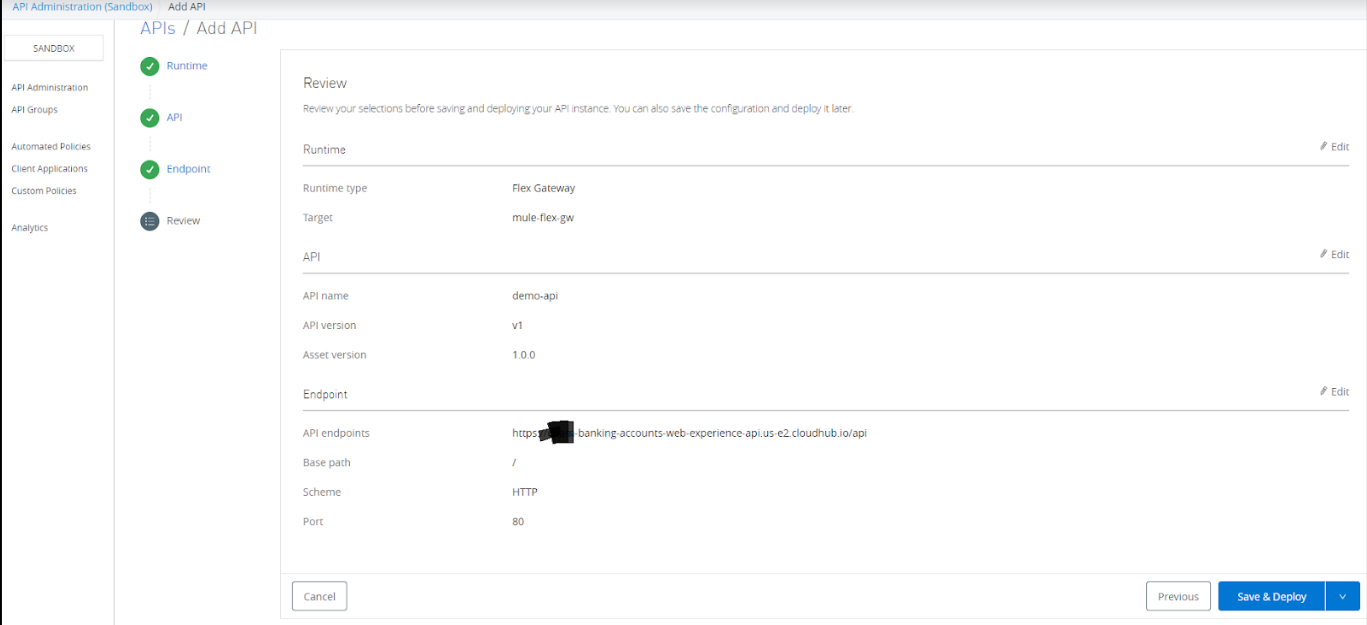
After clicking Next, it will navigate to the review console. We can review all the information and click on the Save & Deploy button.
After the API is successfully published to Flex Gateway, we can see API status to Active in the API Manager console.
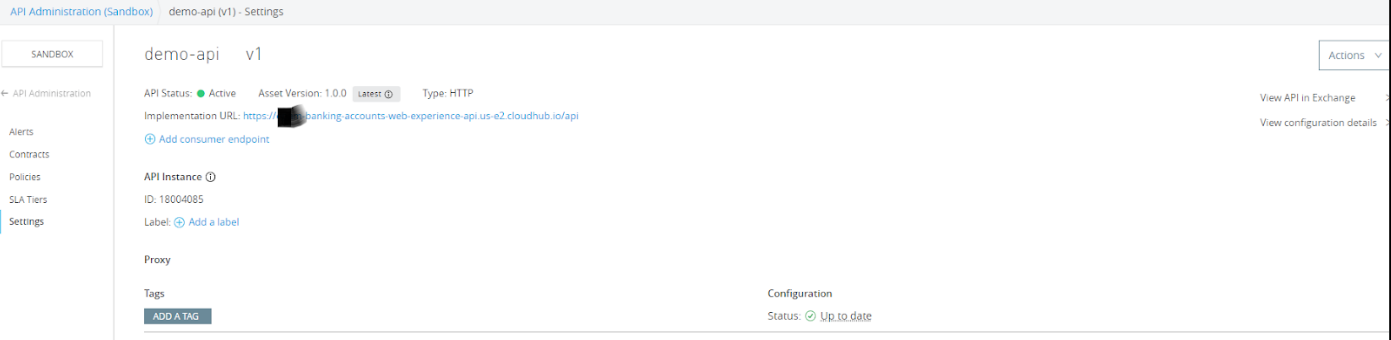
This means API is successfully published to the Flex Gateway.
Accessing APIs published to Flex Gateway on Minikube
As we have already installed the ingress in the part 1 tutorial and will be using ingress for accessing the API. We can execute the below command for getting the ingress URL.
minikube service list --namespace gatewayThis command will give the below output with HTTP and HTTPS URLs. In our case, we have published an API to port 80 and protocol HTTP.
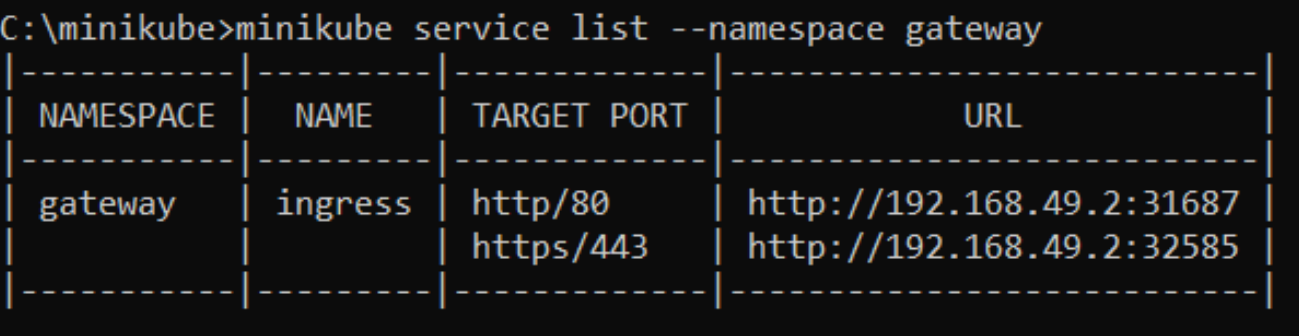
So we will be using a URL that is mapped with HTTP - http://192.168.49.2:31687.
This is a private URL and cannot be accessed outside. In our case, the complete URL will be this.
To access the above private URL, we will open the Minikube container CLI. To do so, just go to docker desktop and open CLI for the Minikube container.
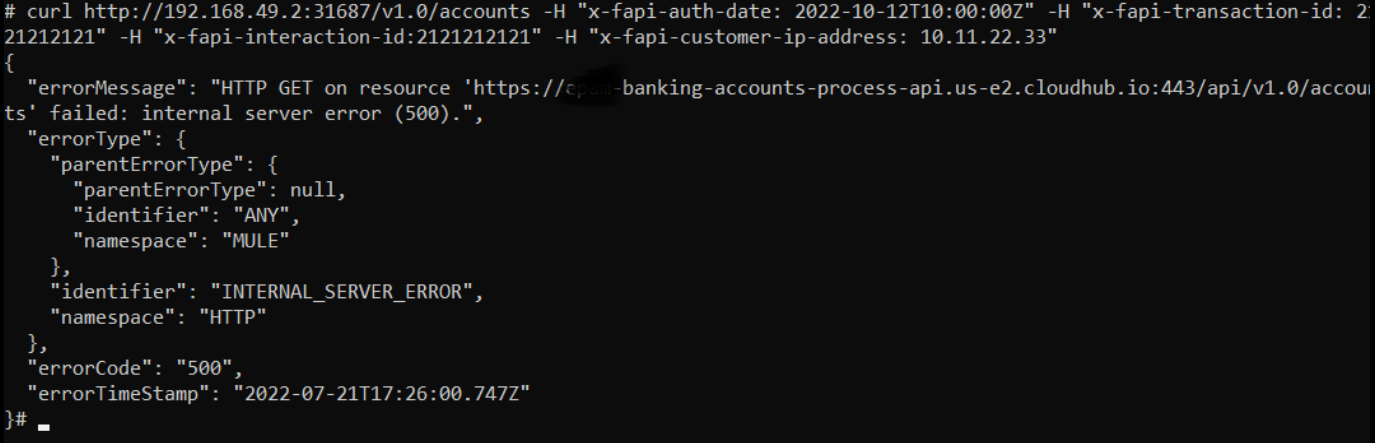
We have curled the above URL and we have got some responses back from our API. This means we have sent a request on ingress and ingress has forwarded the request to the implementation.
If we want to access the URL outside the Minikube, we need to execute the below command and that will provide the URL which can be used to access ingress.
minikube service ingress --url --namespace gatewayThis command will generate the below output with multiple URLs for accessing the ingress.
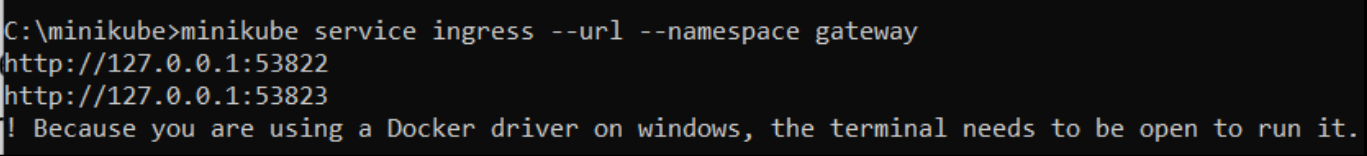
Now, we can use any one of the URLs for accessing the ingress.
This URL can be used in the browser for accessing the APIs. We can see responses from our APIs.
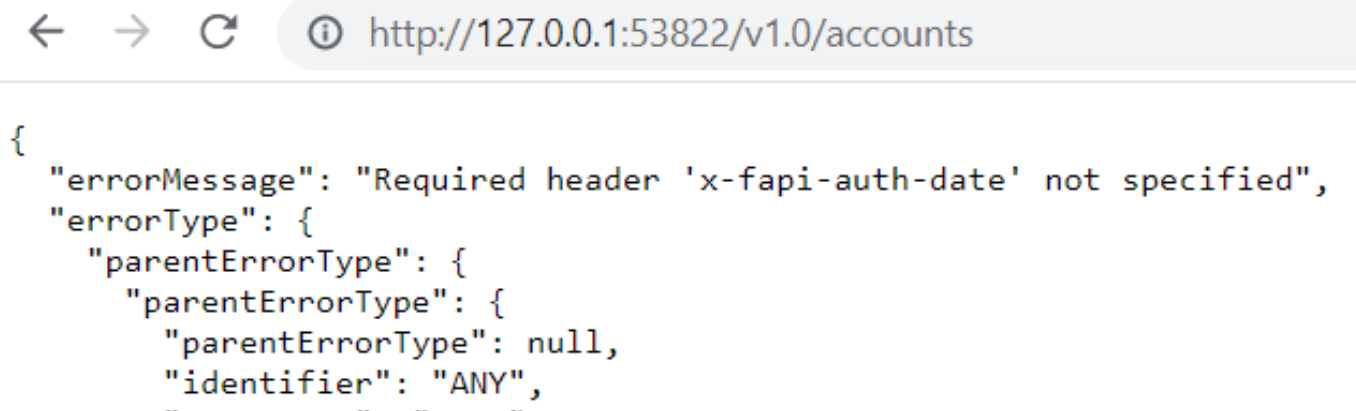
Note - This URL and port number can be different for everyone and everyone's URL may look different.
Please don't confuse by an error response. Here is the intention to show how we can access APIs via Flex Gateway.
Applying Policies to the API
We can use API Manager in the same way that we are using MuleSoft API Gateway for applying the Policies to the API instance. We can apply any out-of-the-box as well as Custom Policies to the APIs.
Navigate to API Manager → Select API Instance → Policies and select whatever policies we need to apply to API instances.
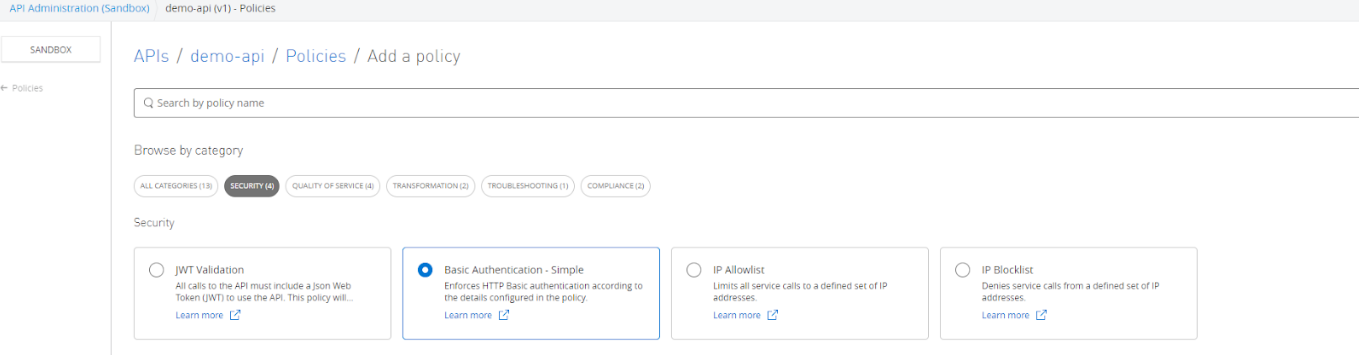
Once policies have been applied, they will be enforced to our APIs deployed to Flex Gateway, and next time whenever we will try to access APIs, it will execute whatever policies applied like it will ask for Authentication in case Basic Authentication or any other security policies have been applied.
API Metrics and Telemetry
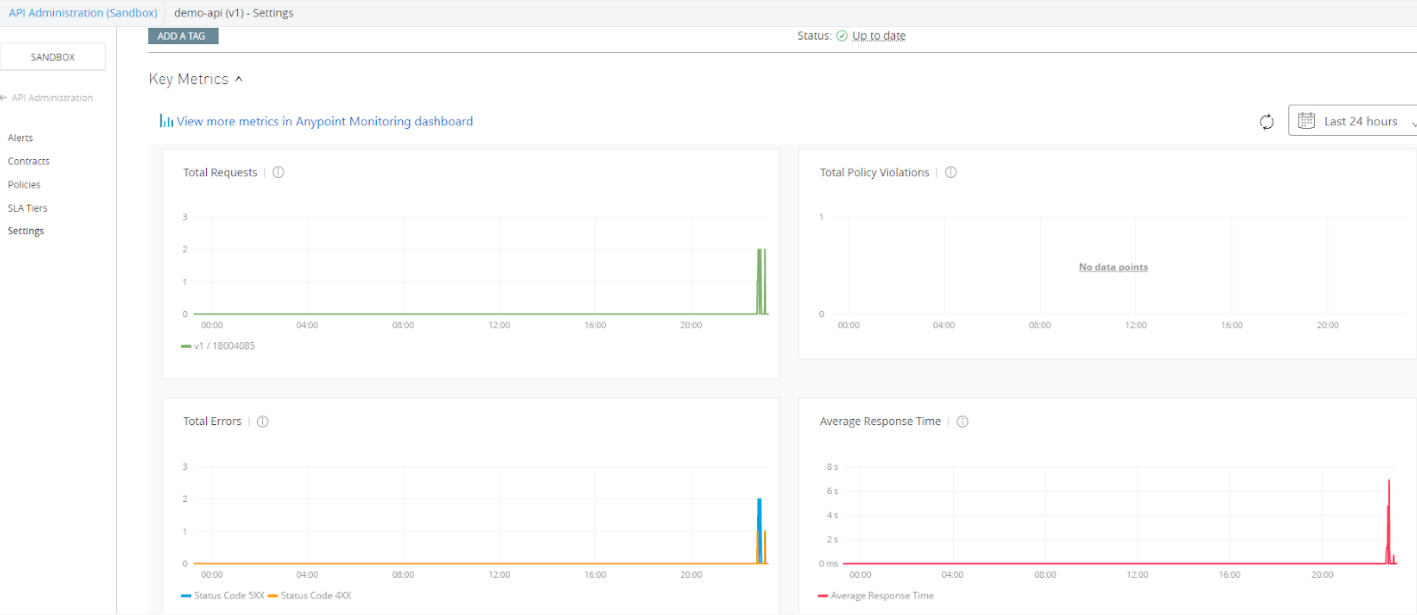
We will see out-of-box API Metrics as part of our API Manager instance. This includes Total Requests, Total Policy Violations, Total Errors, and Average Response Time graphs.
Anypoint Monitoring
When we are using Flex Gateway in Connected Mode, there will be a lot of metrics available that can help us in analyzing or troubleshooting if there are any issues. Anypoint Monitoring provides a lot of details like CPU and Memory Usage, Requests By Response Code, Requests By Method, Average Response Time, etc.
To view metrics on Anypoint Monitoring, navigate to Monitoring, select Environment, Resource name (i.e. API name), Version/Instance, and Click on the View.
Once clicked on the view, it will provide various metrics that can be used for analyzing or troubleshooting any issues.
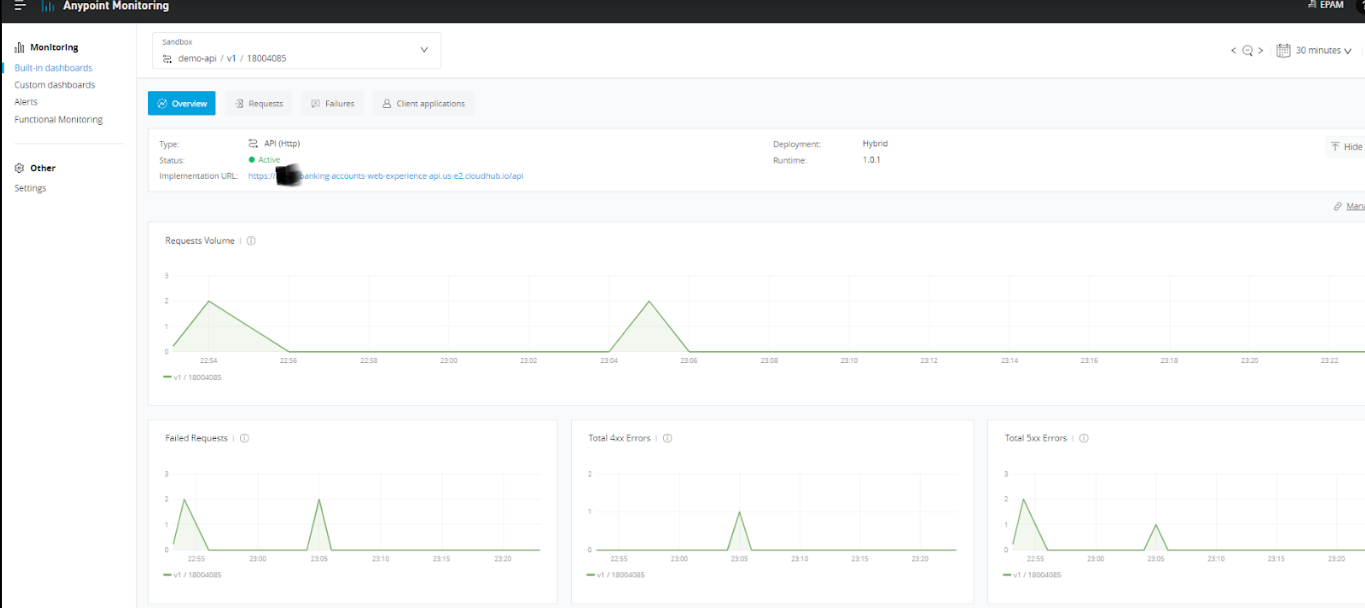
There are out-of-the-box capabilities that can be used with Flex Gateway in Connected Mode like applying API Alerts using API Manager and many other things like Advanced logging etc.
In this tutorial, we have seen how easily APIs can be published to Flex Gateway and easily manage, govern, engage or discover the APIs. Flex Gateway is enabled with various out-of-the-box features and it can easily extend Anypoint API Manager capabilities to any APIs deployed anywhere and written in any technology.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments