Introduction to Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Learn more about the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), as well as important features and types.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBorder Gateway Protocol (BGP) advertises, learns, and chooses the best paths inside the Internet. When two ISPs are connected, they typically use BGP to exchange routing information. The ISPs of the Internet exchange routing information with one or more ISPs.
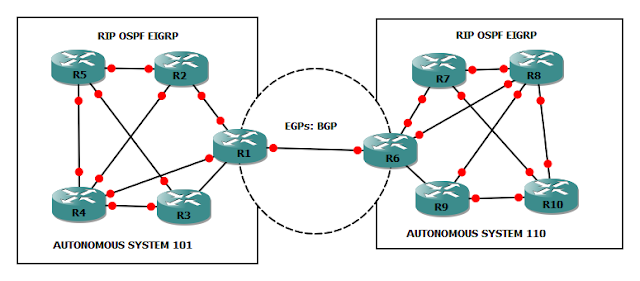
Autonomous System
An autonomous system is a collection of networks under a single technical administration domain. IGPs, like OSPF EIGRP, operate within an autonomous system. We use BGP between the autonomous systems to exchange loop-free routing information.
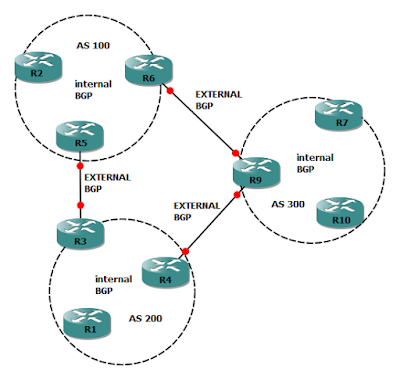
Internal and External BGP
BGP defines two classes for neighbors:
- Internal BGP ( iBGP ) operates within the same autonomous system.
- External BGP ( E BGP) operates inbetween the multiple autonomous system
BGP Features
- BGP is an open standard protocol
- Offers an exterior gateway protocol designed for inter-AS domain routing to scale a huge neter-network, like the Internet
- It supports classless, VLSM, CIDR, auto, and manual summary
- Updates are incremental and trigger the BGP to send updates to a manually-defined neighbor as unicast.
- BGP is an application layer protocol that uses TCP for reliability with TCP port 179
- Metric is attributes
- Administrative distance is 20 for external updates (EBGP) and 200 for internal updates (iBGP)
Types of ISP connections
- Single-homed
- Dual-homed sites
- Multi-homing
- Dual multi-homing
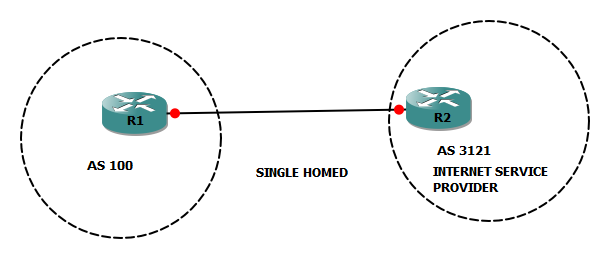
Single-Homed
A single-homed site is a site with a single ISP connection. Single-homed is good for a site that does not depend heavily on the Internet or WAN connectivity. You can advertise the site route or static routes and receive a default route from your Internet service provider.
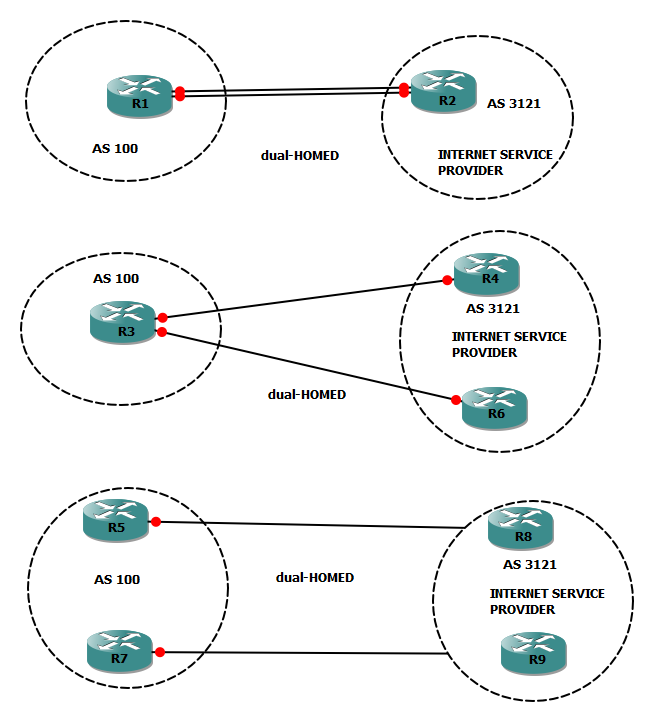
Dual-Homed
A dual-homed site has two connections to the same ISP, either from one router or two routers. One link might be primary and the other is a backup, or the site might be load balancing over both the connections. we can use static or dynamic routing.
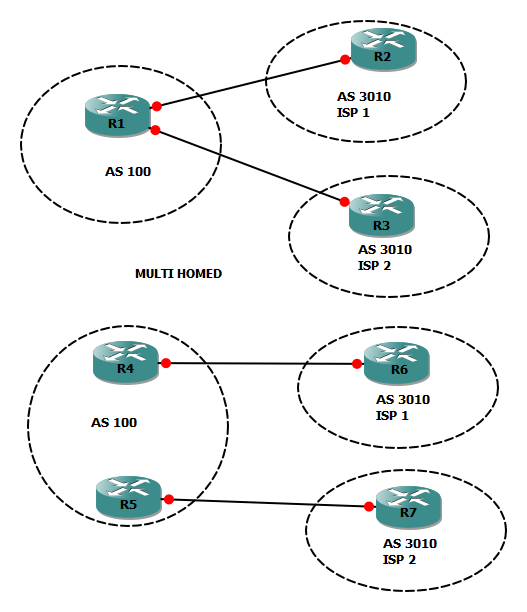
Multi-Homed
Multi-homing means having connecting links to one or more ISPs at the same time. This is done for redundancy and backup in case one ISP fails, and for better performance, if one ISP provides a better path to frequently-used networks, multi-homed also gives you an ISP-independent solution. BGP is typically used with multi-homed connections.
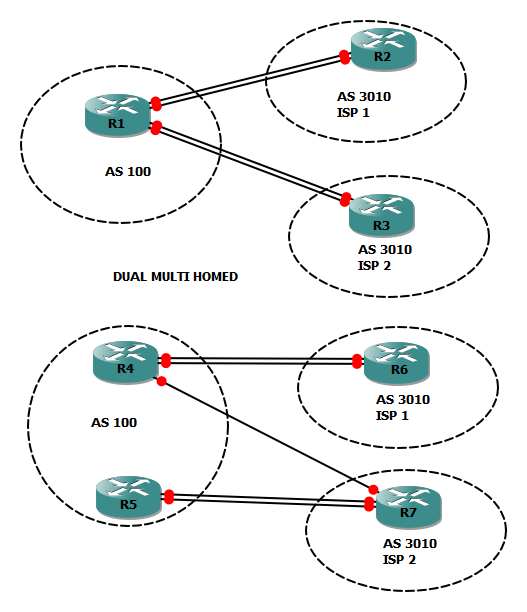
Dual Multi-Homed
Dual multi-homed means having two connections with multiple ISPs. Dual multi-homed gives you the most redundancy. BGP is used with ISPs and can be implemented internally, also.
We hope you enjoyed this post on BGP, as well as its features and types!
Published at DZone with permission of EDGER FRANCIS. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments