Sharing Folders between a VirtualBox Host and Guest Machines
Let's take a look at how to setup folder sharing between a host and VMs in VirtualBox with either Windows or Linux. Read on for the details.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis post is the 4th installment of the VirtualBox series. The focus is on how to share folders between the host and the guest OSes. Part 1 of the series shows how to install VirtualBox on a Debian host, and how to create a FreeBSD virtual machine. Part 2 outlines the post installation tasks, including installing the universal VirtualBox extension pack. Part 3 shows how the guest OS can access USB drives mounted on the host.
The method outlined in this blog post works for Linux and Windows guest OSes but not FreeBSD. You can set up NFS or Samba to share a folder between a Linux host and a FreeBSD guest.
Prerequisites
To share a folder using the following procedure, the OS-specific guest additions package must be pre-installed. Part 1 of this series includes instructions for installing the guest additions package for the FreeBSD guest OS.
Procedure
- Declare the shared folder on host OS.
Open theOracle VM VirtualBox manageron your host machine, select the target guest OS, and clickSettings. Note that your guest machine does NOT need to be powered off.![]()
- Select
Shared Holders, and click thePlusbutton to add a shared folder. Note that you can have more than 1 shared folder.![]()
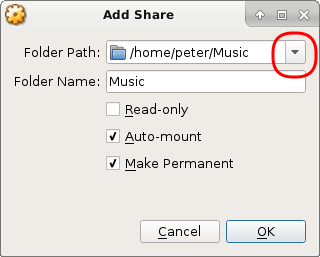
- Specify the path for the shared folder.
Click thedownarrow next to theFolder Pathparameter, selectOther,and navigate to the target shared folder.![]()
- Configure the shared folder.
TheFolder namefield refers to the folder name on the guest OS, which defaults to the folder name you specified in the last step. You should note the folder name in order to identify the full folder pathname on the guest OS. For example, if the shared folder on the host machine is/home/peter/Music, the corresponding folder name defaults to/media/sf_Musicon the Ubuntu guest OS, and\\vboxsvr\Musicon the Windows guest OS.
TheAuto-mountcheckbox should be enabled. Optionally, you can also mount the folder manually, but then you must modify access permissions in order to make the folder writable by non-root users.
Unless the shared folder is for one-off use only, you should enable theMake Permanentcheckbox. - Power recycle the guest machine.
- Grant folder access permission to
non-rootusers.
This step only applies to Linux guest OS(not Windows). Login to the guest OS, and add regular users to thevboxsfgroup using the following command.sudo usermod -aG vboxsf <someuserID>
Published at DZone with permission of Peter Leung, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.




Comments