Struts Migration Strategies
Ready to make the jump to Struts 2? Here is an overview of the differences between Struts 1 and 2 and how to successfully move your projects.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article talks about the strategies for migrating from Struts 1.1 to Struts 2.0. The Struts framework is one of the most popular web application frameworks in the Java EE world. It has been widely adapted in enterprises and has been a de-facto standard for web applications. Of late, there have been few areas where the Struts community felt the need to improve on some of the architectural areas. Hence, a new version of Struts, Struts 2.x, was released. Therefore, existing applications need to migrate from Struts 1.x to Struts 2.x to leverage the enhanced features of Struts without rewriting the whole application. This document is an effort to allow you to do that.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Major changes introduced in Struts 2
Migration Strategies
Migration Steps
Introduction
Struts 1.0
- Officially released in 2001 by Craig McClanahan.
- Provides a unified framework for deploying Servlet and JSP applications using MVC architecture.
Multiple utility classes to handle common tasks.
- Reached EOL (End-Of-Life)
Struts 2.0
Based on the OpenSymphony WebWork2 framework (MVC2 architecture).
Cleaner, extensible, and flexible with annotation-based support.
Support for REST, Ajax, JSON with plugin-based architecture.
Major Changes in Struts 2
- S2 Action Classes are POJOs with execute() instead of mandatorily extending S1 abstract Action classes provided by the framework.
- S2 Actions are thread-safe, as they are instantiated for each request, as compared to S1 Actions, which are singletons.
- S2 Action classes are more testable as compared to S1, as execute() exposes the Servlet API.
- OGNL and Interceptors had been introduced in S2, which makes S1 ActionForms obsolete.
- Convention-over-Configuration support for annotations (e.g. validations).
- An S2 ValueStack feature allows accessing objects without coupling views.
- Enhanced Taglib with support for Ajax.
- Enhanced View technology with support for Velocity and Freemarker templates and XSLT transformations besides JSP.
Struts 1->2 Migration Strategies
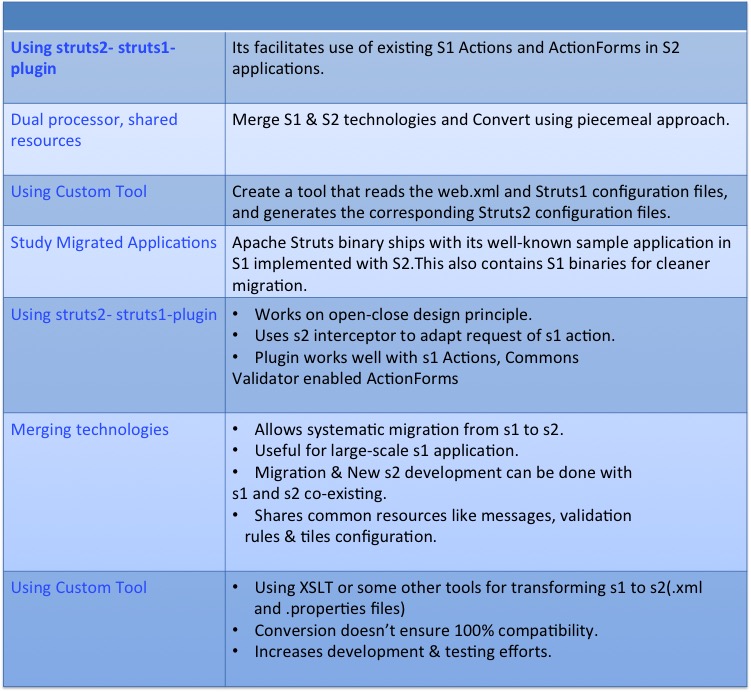
Migration Steps

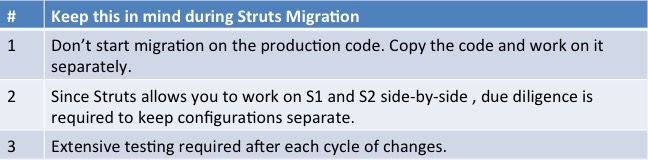
Migration Considerations
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments