Supabase and Angular Quickstart Guide
This example provides the steps to build a simple user management app (from scratch!) using Supabase and Angular.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis example provides the steps to build a simple user management app (from scratch!) using Supabase and Angular. It includes:
- Supabase Database: a Postgres database for storing your user data.
- Supabase Auth: users can sign in with magic links (no passwords, only email).
- Supabase Storage: users can upload a photo.
- Row Level Security: data is protected so that individuals can only access their own data.
- Instant APIs: APIs will be automatically generated when you create your database tables.
By the end of this guide you'll have an app that allows users to log in and update some basic profile details:
 Clicking this button the application will:
Clicking this button the application will:
- Launch and prepare the Postgres database in Supabase.
- Launch the app in Vercel.
- Fork the example into your own GitHub account.
- Prepare the deployed application with all the necessary environment variables.
If you want to do it yourself, let's get started!
GitHub
Whenever you get stuck at any point, take a look at this repo.
Project Set-Up
Before we start building we're going to set up our Database and API. This is as simple as starting a new Project in Supabase and then creating a "schema" inside the database.
Create a Project
- Go to app.supabase.com.
- Click on "New Project".
- Enter your project details.
- Wait for the new database to launch.
Set up the Database Schema
Now we are going to set up the database schema. We can use the "User Management Starter" quickstart in the SQL Editor, or you can just copy/paste the SQL from below and run it yourself.
-- Create a table for public "profiles"
create table profiles (
id uuid references auth.users not null,
updated_at timestamp with time zone,
username text unique,
avatar_url text,
website text,
primary key (id),
unique(username),
constraint username_length check (char_length(username) >= 3)
);
alter table profiles enable row level security;
create policy "Public profiles are viewable by everyone."
on profiles for select
using ( true );
create policy "Users can insert their own profile."
on profiles for insert
with check ( auth.uid() = id );
create policy "Users can update own profile."
on profiles for update
using ( auth.uid() = id );
-- Set up Realtime!
begin;
drop publication if exists supabase_realtime;
create publication supabase_realtime;
commit;
alter publication supabase_realtime add table profiles;
-- Set up Storage!
insert into storage.buckets (id, name)
values ('avatars', 'avatars');
create policy "Avatar images are publicly accessible."
on storage.objects for select
using ( bucket_id = 'avatars' );
create policy "Anyone can upload an avatar."
on storage.objects for insert
with check ( bucket_id = 'avatars' );
UI
1. Go to the "SQL" section.
2. Click "User Management Starter".
3. Click "Run".
Get the API Keys
Now that you've created some database tables, you are ready to insert data using the auto-generated API. We just need to get the URL and anon key from the API settings.
1. Go to the "SQL" section.
2. Click "User Management Starter".
3. Click "Run".
Building the App
Let's start building the Angular app from scratch.
Initialize an Angular App
We can use the Angular CLI to initialize an app called supabase-angular:
npx ng new supabase-angular --routing false --style css
cd supabase-angularThen let's install the only additional dependency: supabase-js
npm install @supabase/supabase-jsAnd finally, we want to save the environment variables in the environment.ts file. All we need are the API URL and the anon key that you copied earlier. These variables will be exposed on the browser, and that's completely fine since we have Row Level Security enabled on our Database.
environment.ts
export const environment = {
production: false,
supabaseUrl: "YOUR_SUPABASE_URL",
supabaseKey: "YOUR_SUPABASE_KEY"
};Now that we have the API credentials in place, let's create a SupabaseService with ng g s supabase to initialize the Supabase client and implement functions to communicate with the Supabase API.
src/app/supabase.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import {AuthChangeEvent, createClient, Session, SupabaseClient} from '@supabase/supabase-js';
import {environment} from "../environments/environment";
export interface Profile {
username: string;
website: string;
avatar_url: string;
}
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class SupabaseService {
private supabase: SupabaseClient;
constructor() {
this.supabase = createClient(environment.supabaseUrl, environment.supabaseKey);
}
get user() {
return this.supabase.auth.user();
}
get session() {
return this.supabase.auth.session();
}
get profile() {
return this.supabase
.from('profiles')
.select(`username, website, avatar_url`)
.eq('id', this.user?.id)
.single();
}
authChanges(callback: (event: AuthChangeEvent, session: Session | null) => void) {
return this.supabase.auth.onAuthStateChange(callback);
}
signIn(email: string) {
return this.supabase.auth.signIn({email});
}
signOut() {
return this.supabase.auth.signOut();
}
updateProfile(profile: Profile) {
const update = {
...profile,
id: this.user?.id,
updated_at: new Date()
}
return this.supabase.from('profiles').upsert(update, {
returning: 'minimal', // Don't return the value after inserting
});
}
downLoadImage(path: string) {
return this.supabase.storage.from('avatars').download(path);
}
uploadAvatar(filePath: string, file: File) {
return this.supabase.storage
.from('avatars')
.upload(filePath, file);
}
}
And one optional step is to update the CSS file src/index.css to make the app look nice. You can find the full contents of this file here.
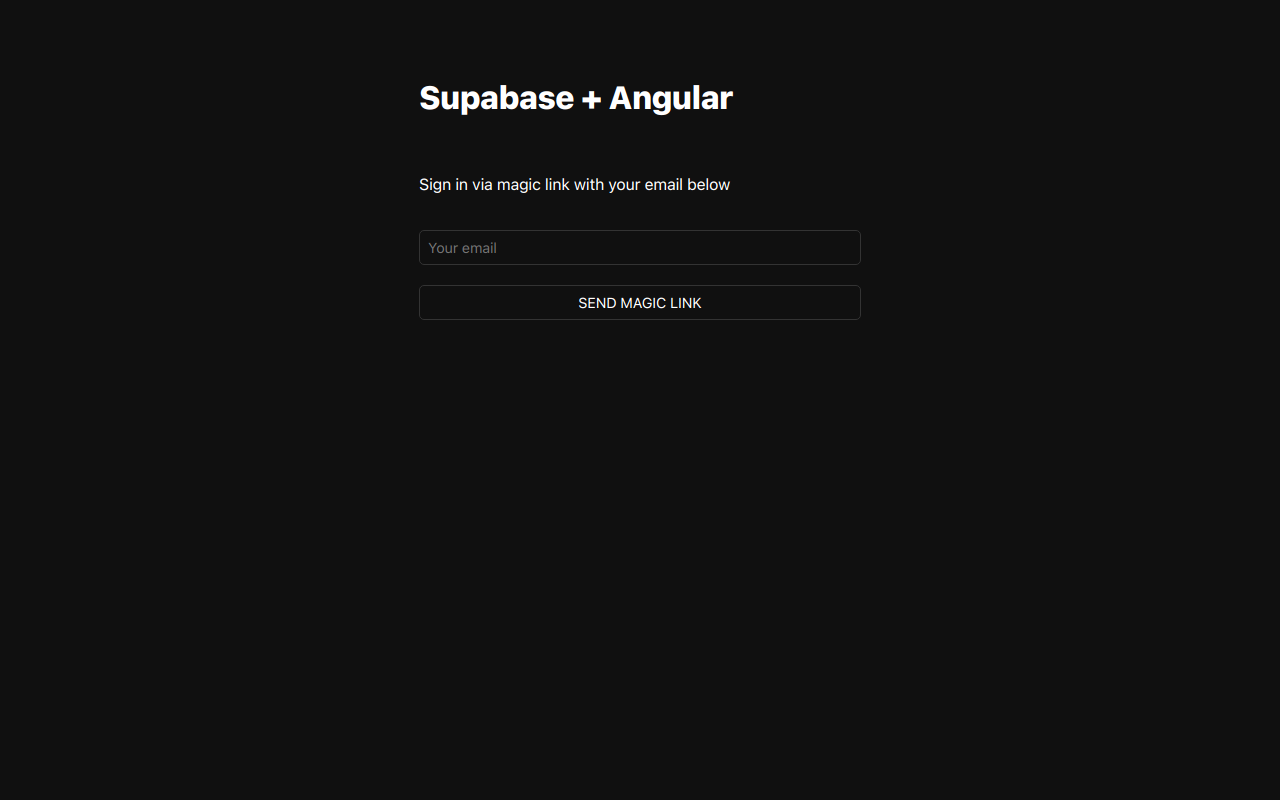
Set up a Login Component
Let's set up an Angular component to manage logins and sign-ups. We'll use Magic Links, so users can sign in with their email without using passwords. Create an AuthComponent with ng g c auth Angular CLI command.
src/app/auth.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import {SupabaseService} from "./supabase.service";
@Component({
selector: 'app-auth',
template: `
<div class="row flex flex-center">
<form class="col-6 form-widget">
<h1 class="header">Supabase + Angular</h1>
<p class="description">Sign in via magic link with your email below</p>
<div>
<input
#input
class="inputField"
type="email"
placeholder="Your email"
/>
</div>
<div>
<button
type="submit"
(click)="handleLogin(input.value)"
class="button block"
[disabled]="loading"
>
{{loading ? 'Loading' : 'Send magic link'}}
</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
`,
})
export class AuthComponent {
loading = false;
constructor(private readonly supabase: SupabaseService) { }
async handleLogin(input: string) {
try {
this.loading = true;
await this.supabase.signIn(input);
alert('Check your email for the login link!');
} catch (error) {
alert(error.error_description || error.message)
} finally {
this.loading = false;
}
}
}Account Page
After a user is signed in we can allow them to edit their profile details and manage their account. Create an AccountComponent with ng g c account Angular CLI command.
src/app/account.component.ts
import {Component, Input, OnInit} from '@angular/core';
import {Profile, SupabaseService} from "./supabase.service";
import {Session} from "@supabase/supabase-js";
@Component({
selector: 'app-account',
template: `
<div class="form-widget">
<div>
<label for="email">Email</label>
<input id="email" type="text" [value]="session?.user?.email" disabled/>
</div>
<div>
<label for="username">Name</label>
<input
#username
id="username"
type="text"
[value]="profile?.username ?? ''"
/>
</div>
<div>
<label for="website">Website</label>
<input
#website
id="website"
type="url"
[value]="profile?.website ?? ''"
/>
</div>
<div>
<button
class="button block primary"
(click)="updateProfile(username.value, website.value)"
[disabled]="loading"
>
{{loading ? 'Loading ...' : 'Update'}}
</button>
</div>
<div>
<button class="button block" (click)="signOut()">
Sign Out
</button>
</div>
</div>
`
})
export class AccountComponent implements OnInit {
loading = false;
profile: Profile | undefined;
@Input() session: Session | undefined;
constructor(private readonly supabase: SupabaseService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.getProfile();
}
async getProfile() {
try {
this.loading = true;
let {data: profile, error, status} = await this.supabase.profile;
if (error && status !== 406) {
throw error;
}
if (profile) {
this.profile = profile;
}
} catch (error) {
alert(error.message)
} finally {
this.loading = false;
}
}
async updateProfile(username: string, website: string, avatar_url: string = '') {
try {
this.loading = true;
await this.supabase.updateProfile({username, website, avatar_url});
} catch (error) {
alert(error.message);
} finally {
this.loading = false;
}
}
async signOut() {
await this.supabase.signOut();
}
}Launch!
Now that we have all the components in place, let's update AppComponent:
src/app/app.component.ts
import {Component, OnInit} from '@angular/core';
import {SupabaseService} from "./supabase.service";
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<div class="container" style="padding: 50px 0 100px 0">
<app-account *ngIf="session; else auth" [session]="session"></app-account>
<ng-template #auth>
<app-auth></app-auth>
</ng-template>
</div>
`
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
session = this.supabase.session;
constructor(private readonly supabase: SupabaseService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.supabase.authChanges((_, session) => this.session = session);
}
}Once that's done, run this in a terminal window: npm run start
And then open the browser to localhost:4200 and you should see the completed app.
Bonus: Profile Photos
Every Supabase project is configured with Storage for managing large files like photos and videos.
Create an Upload Widget
Let's create an avatar for the user so that they can upload a profile photo. Create an AvatarComponent with ng g c avatar Angular CLI command.
src/app/avatar.component.ts
import {Component, EventEmitter, Input, Output} from '@angular/core';
import {SupabaseService} from "./supabase.service";
import {DomSanitizer, SafeResourceUrl} from "@angular/platform-browser";
@Component({
selector: 'app-avatar',
template: `
<div>
<img
*ngIf="_avatarUrl"
[src]="_avatarUrl"
alt="Avatar"
class="avatar image"
style="height: 150px; width: 150px"
></div>
<div *ngIf="!_avatarUrl" class="avatar no-image" style="height: 150px; width: 150px"></div>
<div style="width: 150px">
<label class="button primary block" for="single">
{{uploading ? 'Uploading ...' : 'Upload'}}
</label>
<input
style="visibility: hidden;position: absolute"
type="file"
id="single"
accept="image/*"
(change)="uploadAvatar($event)"
[disabled]="uploading"
/>
</div>
`,
})
export class AvatarComponent {
_avatarUrl: SafeResourceUrl | undefined;
uploading = false;
@Input()
set avatarUrl(url: string | undefined) {
if (url) {
this.downloadImage(url);
}
};
@Output() upload = new EventEmitter<string>();
constructor(
private readonly supabase: SupabaseService,
private readonly dom: DomSanitizer
) { }
async downloadImage(path: string) {
try {
const {data} = await this.supabase.downLoadImage(path);
this._avatarUrl = this.dom.bypassSecurityTrustResourceUrl(URL.createObjectURL(data));
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error downloading image: ', error.message);
}
}
async uploadAvatar(event: any) {
try {
this.uploading = true;
if (!event.target.files || event.target.files.length === 0) {
throw new Error('You must select an image to upload.');
}
const file = event.target.files[0];
const fileExt = file.name.split('.').pop();
const fileName = `${Math.random()}.${fileExt}`;
const filePath = `${fileName}`;
await this.supabase.uploadAvatar(filePath, file);
this.upload.emit(filePath);
} catch (error) {
alert(error.message);
} finally {
this.uploading = false;
}
}
}Add the New Widget
And then we can add the widget on top of the AccountComponent HTML template:
src/app/account.component.ts
template: `
<app-avatar
[avatarUrl]="this.profile?.avatar_url"
(upload)="updateProfile(username.value, website.value, $event)">
</app-avatar>
<!-- input fields -->
`Next Steps
At this stage, you have a fully functional application!
- Got a question? Ask here.
- Sign in: app.supabase.com.
Published at DZone with permission of Rory Wilding. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments