Deep Dive Into OCR for Receipt Recognition
No matter what you choose, an LSTM or another complex method, there is no silver bullet. Some methods are hard to use and not always useful.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeOptical Character Recognition is a process when images of handwritten, printed, or typed text are converted into machine-encoded text. Automated recognition of documents, credit cards, car plates and billboards significantly simplifies the way we collect and process data.
The growth of Machine Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) has helped text recognition make a huge leap forward. We used CNN in our research to recognize paper receipts from retail stores. The system can be adjusted to process different languages, but we tested it using Russian.
The goal of our project was to develop an app using the client-server architecture for receipt recognition. Let's take a closer look, step by step.
Preprocessing
First things first: we rotated the receipt image so that the text lines were horizontally oriented, made the algorithm detect the receipt, and binarized it.
Rotating Image to Recognize a Receipt
What we used to recognize a receipt on the image:
Adaptive binarization with a high threshold.
Convolutional Neural Network.
Haar cascade classifier.
Using Adaptive Binarization

First, we recognized the area on the image that contains the full receipt and almost no background. To achieve this, we rotated the image so that text lines are horizontally oriented.
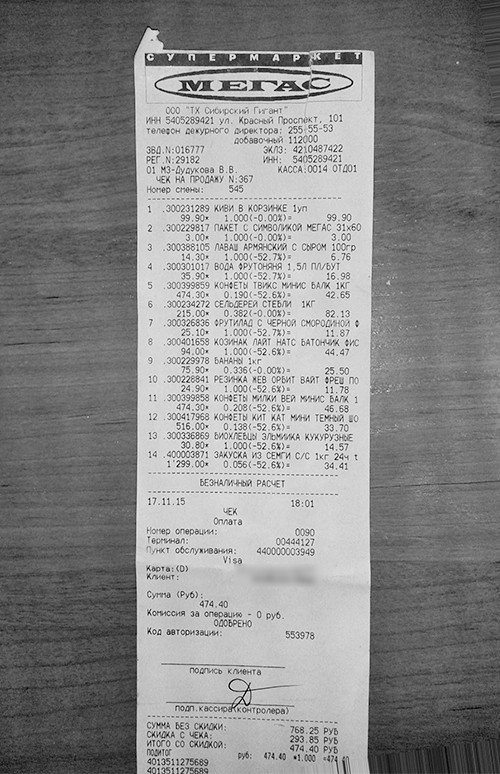
We used the adaptive_threshold function from the scikit-image library to find the receipt. This function keeps white pixels in areas with a high gradient, while more homogeneous areas turn black. Using this function, we got a homogeneous background with a couple of white pixels. We were searching for them to define the rectangle.
Using a CNN
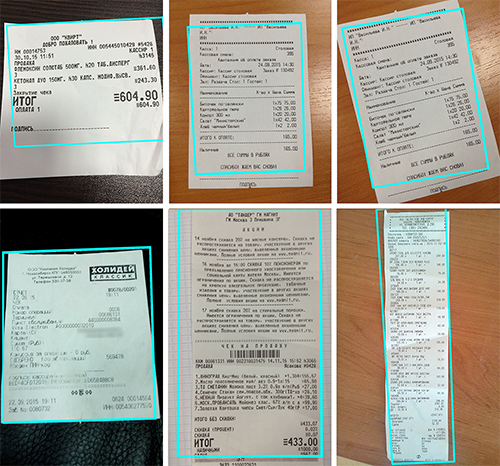
We decided to find receipt keypoints using a convolutional neural network as we did before for the object detection project. We chose the receipt angles as key points. This method performed well, but worse than adaptive binarization with a high threshold.
The CNN was able to define only those angle coordinates relative to the found text. Text to angle orientation varies greatly, meaning this CNN model is not very precise.
See CNN results below.
Using the Haar Cascade Classifier to Recognize a Receipt
As a third alternative, we tried the Haar cascade classifier. However, after a week of training the classifier and changing recognition parameters, we didn’t get any positive result. Even the CNN performed much better.
Haar cascade classifier results:


Binarization
In the end, we used the same adaptive_threshold method for binarization. The window is quite big so that it contains the text as well as the background.
Text Detection
Let's cover a few different components of text detection.
Detecting Text Via Connected Components
First, we found the connected components using the findContours function from OpenCV. The majority of connected components are characters, but a few are just noisy text fragments left after binarization. We filtered them using maximal/minimal axis.
Then we applied a combining algorithm to compound characters, like :, Й, and =. The characters are then combined into words via a nearest neighbour search. Here is the principle of nearest neighbours method. You need to find the closest neighbor for every character. Then you choose the most appropriate candidate for combination from the right and from the left side. The algorithm is processed until there are no more characters left.
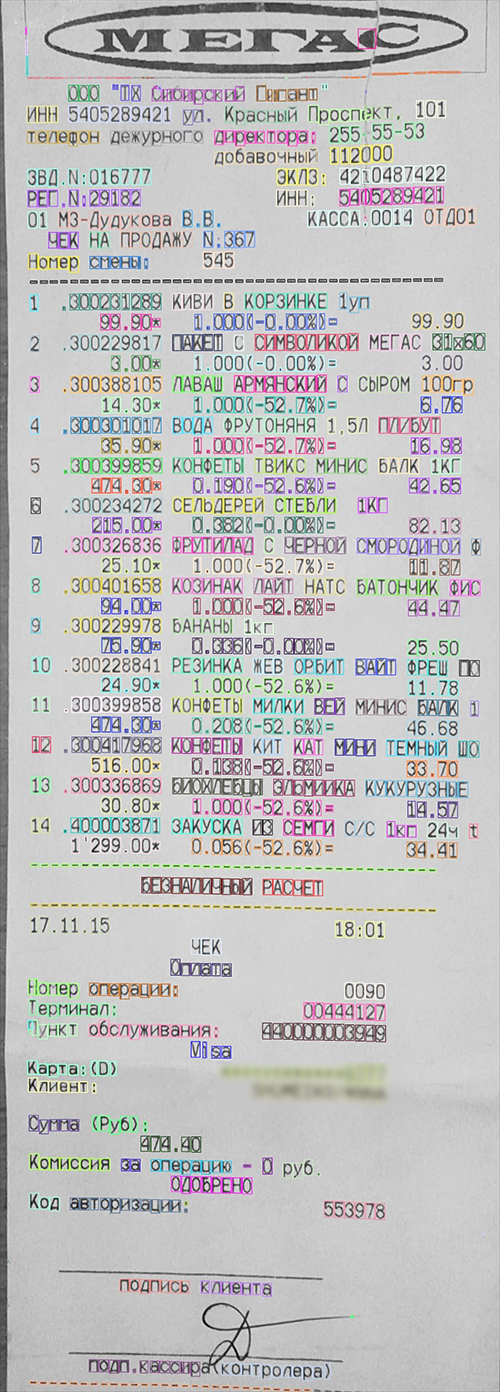
Then words formed text lines. We used the hypothesis that words in a single line are located at the same height.

The disadvantage is that this algorithm cannot correctly recognize noisy text.
Using a Grid for Text Detection
We found that almost all receipts had monospaced text. So we managed to draw a grid on the receipt and separate characters from each other using grid lines:
The grid simplifies further receipt recognition. A neural network can be applied to every cell of the grid and every character can be easily recognized. The problem of noisy text is gone. Finally, the number of consequent spaces was precisely defined.
We tried the following algorithm to recognize the grid. First, we found connected components in the binary image:
Then we processed the lower-left angles of the green rectangles and got a set of points specified by coordinates. To determine distortions we used the 2d periodic function:
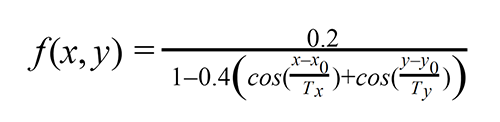
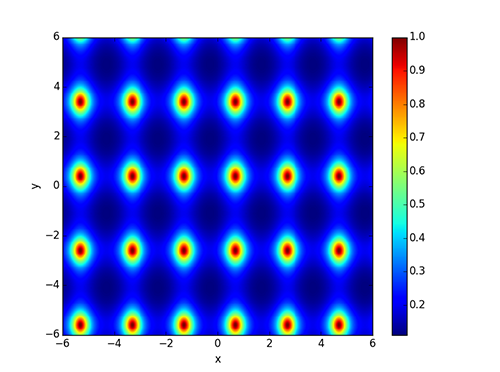
The main idea behind the receipt grid was to find non-linear geometric distortions with the graph peak points. In other words, we had to find the maximum value sum of this function. Also, we needed to find an optimal distortion.
We parametrized a geometric distortion using the RectBivariateSpline function from the Scipy Python module. We used the minimize Scipy function for optimization.
Here’s what we got:

All in all, this method appeared to be slow and unstable. We decided not to use it again.
Optical Character Recognition
Let's deal with recognizing text we found via connected components and recognizing complete words.
Recognizing Text We Found Via Connected Components
For text recognition, we used a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) trained on receipt fonts. As an output, we had probabilities for every character. We took several initial options that together had 99% probability. Then we used a dictionary to check all possible words that can be compiled using these characters. This helped improve the recognition accuracy and eliminate faults caused by similar characters (for example, "З" and "Э", Cyrillic alphabet).

However, the method’s performance is very low when it comes to noisy text recognition.
Recognizing Complete Words
It is necessary to recognize complete words when a text is too noisy to recognize it by single characters. We solved this problem using two methods:
LSTM network.
Uniform segmentation.
LSTM Network
You can read these articles to learn more about reading text in deep convolutional sequences and using LSTM networks for language-independent OCR. For this purpose, we used the OCRopus library.
We used monospaced fonts and prepared an artificial sample for training.
After the training, we tested our network using a validation set. The test result appeared to be positive. Then we tested it using real receipts. Here is what we got:

The trained neural network performed well on simple examples. We successfully recognized them before using other methods. The network didn’t work for complex cases.
We distorted the training sample and approximated it to the words recognized on receipts.
 To avoid network overfitting we stopped the training process several times and continued training the network with the new dataset. Finally, we got the following results:
To avoid network overfitting we stopped the training process several times and continued training the network with the new dataset. Finally, we got the following results:

Our new network was good at recognizing complex words. But simple word recognition was not so good.
We believe this CNN can perform much better with a single font and minor distortions.
Uniform Segmentation
The receipts font was monospaced, so we decided to split the words by characters. First, we needed to know the width of every character. Thus, the mode of the character width was estimated for every receipt. In the case of a bimodal character width distribution, there are two modes chosen and a specific width is picked for every text line.
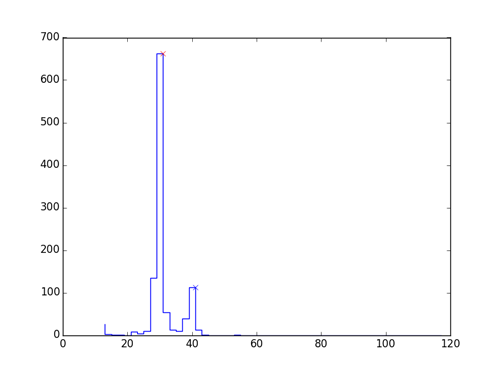
When we got an approximate character width, we divided the length of the word by the character width to get the approximate number of characters. Then we divided the length of the word by the approximate number of characters, give or take one character:
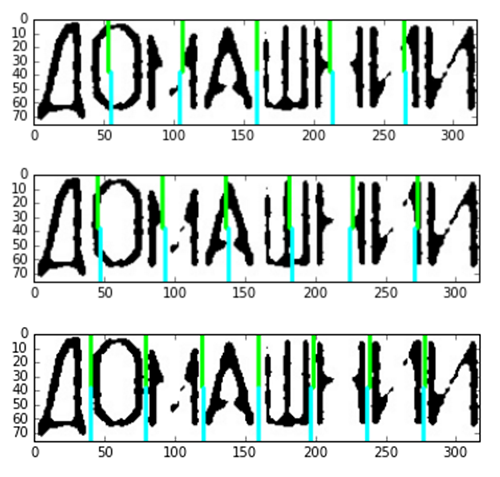
Choosing the best option for division:

The accuracy of such segmentation is quite high.
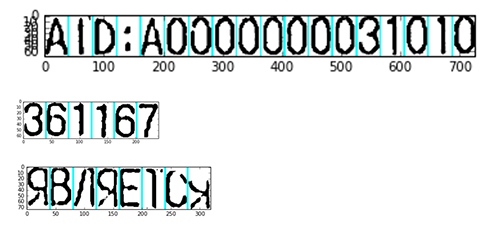
Sometimes our algorithms performed incorrectly:

Every fragment was processed by a CNN after the segmentation.
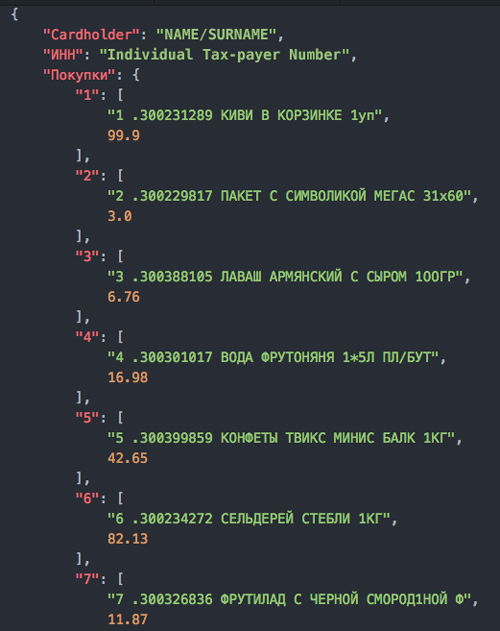
Extracting Meaning From Receipts
We used regular expressions to find purchases in receipts. There is one feature in common for all the receipts: the price of purchases is written in the XX.XX format, where X is a number. Therefore, it’s possible to extract the lines containing purchases. The Individual Taxpayer Number can be found by searching for 10 numbers and tested by the control sum. The Cardholder Name has the format NAME/SURNAME.
Takeaways
No matter what you choose, an LSTM or another complex method, there is no silver bullet. Some methods are hard to use and not always useful.
We'll continue working on the project. For now, the system shows good performance when the recognized text is not noisy.
Published at DZone with permission of Ivan Ozhiganov. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments