Apache Flink Basic Transformation Example
Apache Flink helps build big data in a efficient and scalable way. Learn how to use it to read data from a file, transform it to uppercase, and write it to another file.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeApache Flink is a stream processing framework with added capabilities such as batch processing, graph algorithms, machine learning, reports, and trends insight. Using Apache Flink can help you build a vast amount of data in a very efficient and scalable manner.
In this article, we'll be reading data from a file, transforming it to uppercase, and writing it into a different file.
Gradle Dependencies
dependencies {
compile "org.apache.flink:flink-java:1.4.2"
compile "org.apache.flink:flink-streaming-java_2.11:1.4.2"
compile "org.apache.flink:flink-clients_2.11"
}Core Concept of Flink API
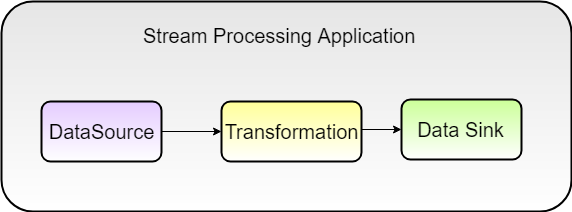
When working with the Flink API:
- DataSource represents a connection to the original data source.
- Transformation represents what needs to be performed on the events within the data streams. A variety of functions for transforming data are provided, including filtering, mapping, joining, grouping, and aggregating.
- Data sink triggers the execution of a stream to produce the desired result of the program, such as saving the result to the file system, printing it to the standard output, writing to the database, or writing to some other application.
The data source and data sink components can be set up easily using built-in connectors that Flink provides to different kinds of sources and sinks.
Flink transformations are lazy, meaning that they are not executed until a sink operation is invoked.
Code:
package com.uppi.poc.flink;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.utils.ParameterTool;
import org.apache.flink.core.fs.FileSystem.WriteMode;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
public class UpperCaseTransformationApp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DataStream < String > dataStream = null;
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args);
env.getConfig().setGlobalJobParameters(params);
if (params.has("input") && params.has("output")) {
//data source
dataStream = env.readTextFile(params.get("input"));
} else {
System.err.println("No input specified. Please run 'UpperCaseTransformationApp --input <file-to-path> --output <file-to-path>'");
return;
}
if (dataStream == null) {
System.err.println("DataStream created as null, check file path");
System.exit(1);
return;
}
//transformation
SingleOutputStreamOperator < String > soso = dataStream.map(String::toUpperCase);
//data sink
soso.writeAsText(params.get("output"), WriteMode.OVERWRITE);
env.execute("read and write");
}
}DataSet API Transformation
As you can see, dataStream is initialized as null but later, we will create it.
DataStream<String> dataStream=null;Initializing Flink Environment
The next step is to initialize stream execution environment by calling this helper method:
StreamExecutionEnvironment. getExecutionEnvironment()Flink figures out which environment you submitted (whether it is a local environment or cluster environment).
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env =
StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();Data Stream Creation
To get the data stream from the data source, just call the built-in Flink API method readTextFile() from StreamExecutionEnvironment. This method reads file content from a given file and returns it as a dataStream object.
Example:
dataStream.readTextFile(params.get("input"));ParameterTools
The ParamerterTools class represents user command line arguments. Example:
$ flink run flink-basic-example-1.0.jar --input c:\tools\input.txt--output c:\tools\output.txtWe need to send all command line arguments to execution environment by calling:
env.getConfig().setGlobalJobParameters(params);Writing Output to Data Sink
printn(): The data stream print method writes each entity of the data stream to a Flink log file.
writeAsText(): This method has two arguments: the first argument is the output file/path and the second argument is writer mode.
Example:
soso.writeAsText(params.get("output"),WriteMode.OVERWRITE);Trigger Flow Execution
All actions specified earlier will happen. If you don’t call the execute method, your program will complete without doing anything. When calling the execute method, you can specify the name of the job. Example:
env.execute("read and write");Running Flink Application
Step 1: Clone the project from GitHub and run the Gradle command > gradlew clean build. Once the build is a success, it generates a flink-basic-example-1.0.jar file in the current project folder's /build/libs directory.
Step 2: Run the Flink server on Windows with start-local.bat.
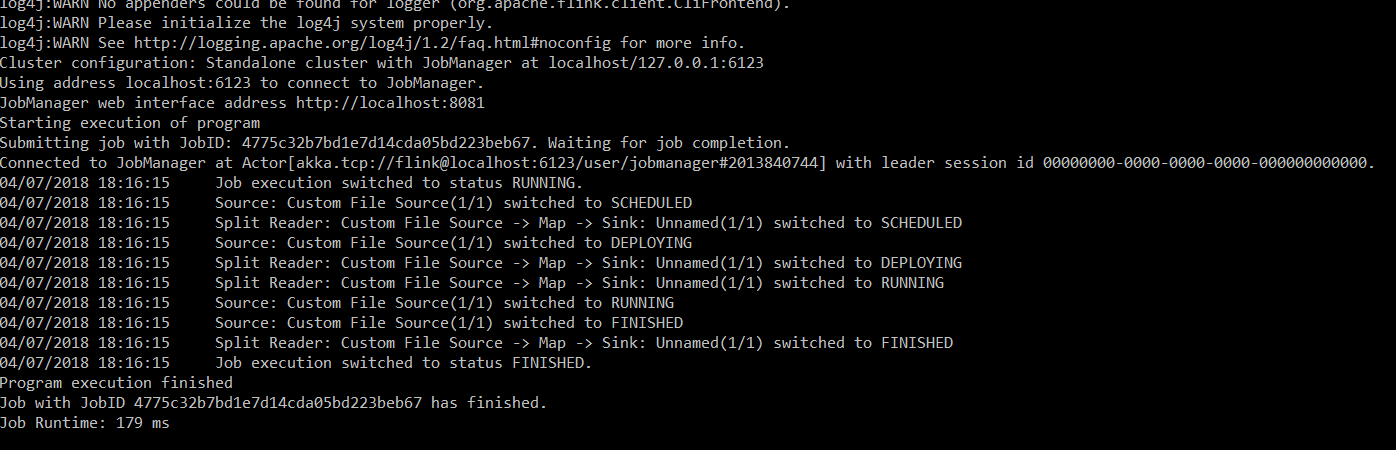
Step 3: Run your own Flink application command line by going to the Flink installation folder and type the following command:
flink run <path-to-jar-file> --input <path-to-file> --output <path-to-file>Example:

input.txt:
training in Big Data Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Flink, Apache Kafka, Hbase, Apache Hadoop Adminoutput.txt:
TRAINING IN BIG DATA HADOOP, APACHE SPARK, APACHE FLINK, APACHE KAFKA, HBASE, APACHE HADOOP ADMINStep 5: Running the Flink application using the Flink web UI. Typelocalhost:8081(by default, Flink runs on port 8081).
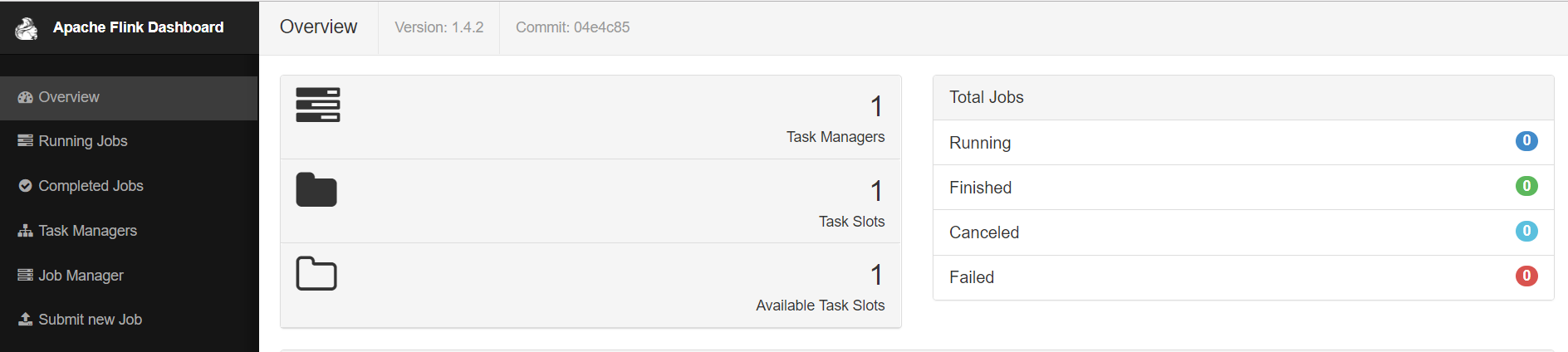
Click Submit New Job > Add New Task and upload generated JAR file. This JAR lets you generate with:
gradlew clean build (jar location - /build/libs)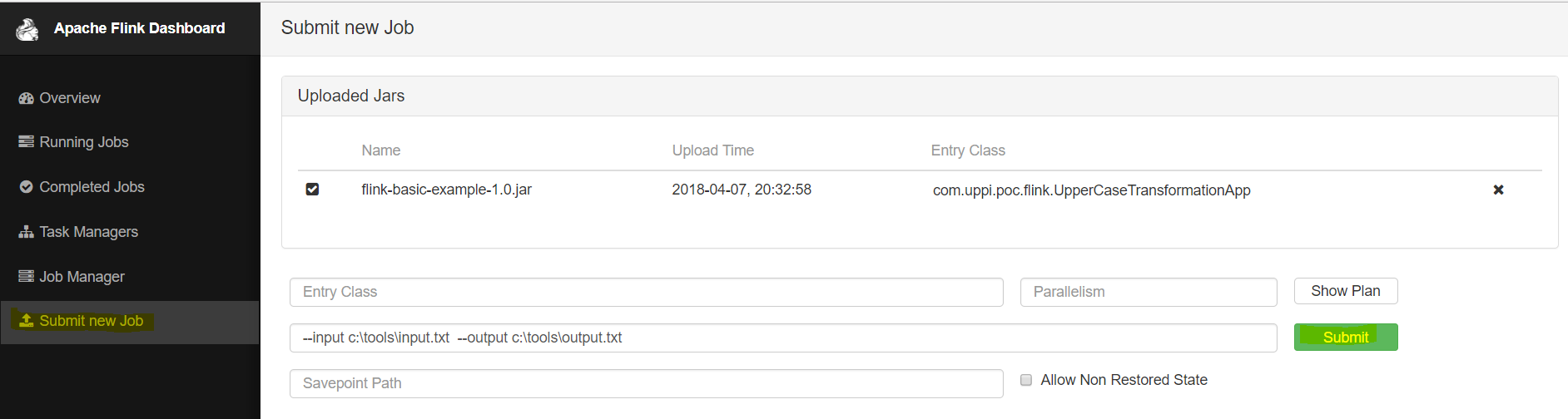
Just enter the program arguments input box as:
--input <path-to-file> --output <path-to-file>And hit Submit. After running the job, you will see the below screen if you hit Completed Jobs.
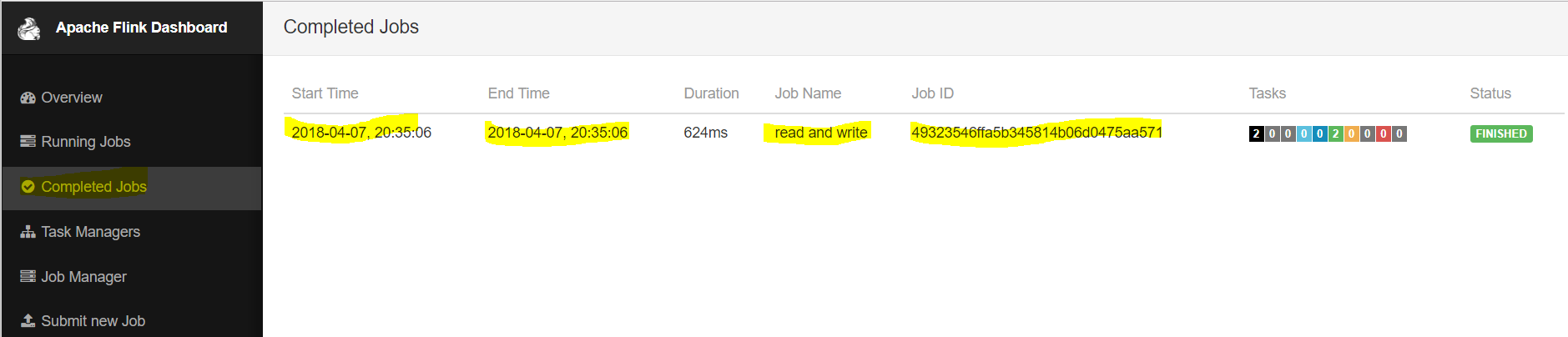
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments