Java - How to Create a Binary Search Tree
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freethis article represents the high level concept and code samples which could be used to create a binary search tree in java. please feel free to comment/suggest if i missed to mention one or more important points. also, sorry for the typos.
following are the key points described later in this article:
- what is a binary search tree?
- what are different kind of traversals?
- code samples
what is a binary search tree?
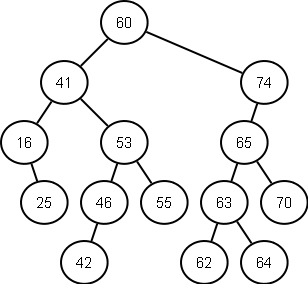
a binary search tree is a binary tree in which every node contains a key that satisfies following criteria:
- the key in left child is less than the key in the parent node
- the key in the right child is more than the parent node
- the left and right child are again binary search trees.
following diagram represents a binary search tree:
what are different kind of traversals?
following are three different kind of traversals:
- preorder traversal : in preorder traversal, the node is visted first and then, left and right sub-trees.
- inorder traversal : in inorder traversal, the node is visited between left and right sub-tree.
- postorder traversal : in postorder traversal, the node is visited after left and right subtrees.
code sample – how to create a binary search tree
if the numbers such as {20, 15, 200, 25, -5, 0, 100, 20, 12, 126, 1000, -150} are to be stored in a binarytree (represented by code below), following would get printed using different kind of traversal mechanism:
//preorder traversal 20, 15, -5, -150, 0, 12, 200, 25, 20, 100, 126, 1000 // inorder traversal -150, -5, 0, 12, 15, 20, 20, 25, 100, 126, 200, 1000 //postorder traversal -150, 12, 0, -5, 15, 20, 126, 100, 25, 1000, 200, 20
following is the code for creating binary tree that uses following binarytree class and traversals:
binarytree tree = new binarytree( 20 );
int[] nums = {15, 200, 25, -5, 0, 100, 20, 12, 126, 1000, -150};
for(int i : nums ) {
tree.addnode( i );
}
tree.traversepreorder();
tree.traverseinorder();
tree.traversepostorder();
following is the code for binarytree class:
public class binarytree {
private int data;
private binarytree left;
private binarytree right;
public binarytree(int num) {
this.data = num;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
// as a convention, if the key to be inserted is less than the key of root node, then key is inserted in
// left sub-tree; if key is greater, it is inserted in right sub-tree. if it is equal, as a convention, it
// is inserted in right sub-tree
public void addnode(int num) {
if (num < this.data) {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.addnode(num);
} else {
this.left = new binarytree(num);
}
} else {
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.addnode(num);
} else {
this.right = new binarytree(num);
}
}
}
// visit the node first, then left and right sub-trees
public void traversepreorder() {
system.out.println( this.data );
if( this.left != null ) {
this.left.traversepreorder();
}
if( this.right != null ) {
this.right.traversepreorder();
}
}
// visit left sub-tree, then node and then, right sub-tree
public void traverseinorder() {
if( this.left != null ) {
this.left.traverseinorder();
}
system.out.println( this.data );
if( this.right != null ) {
this.right.traverseinorder();
}
}
// visit left sub-tree, then right sub-tree and then the node
public void traversepostorder() {
if( this.left != null ) {
this.left.traversepostorder();
}
if( this.right != null ) {
this.right.traversepostorder();
}
system.out.println( this.data );
}
}
Published at DZone with permission of Ajitesh Kumar, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments