MapReduce and Yarn: Hadoop Processing Unit Part 1
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
In my previous article, HDFS Architecture and Functionality, I’ve described the filesystem of Hadoop. Today, we will be learning about the processing unit of it. There are mainly two mechanisms by which processing takes place in a Hadoop cluster, namely, MapReduce and YARN. In our traditional system, the major focus is on bringing data to the storage unit. In the Hadoop process, the focus is shifted towards bringing the processing power to the data to initiate parallel processing. So, here, we will be going through MapReduce and, in part two, YARN.
Mapreduce
As the name suggests, processing mainly takes place in two steps, mapping and reducing. There is a single master (Job tracker) that controls ob execution on multiple slaves (Task tracker). The Job Tracker accepts MapReduce jobs submitted by the client. It pushes a map and reduce tasks out to Task Tracker and also monitors their status. Task trackers' major function is to run the map and reduce tasks. They also manage and store the intermediate output of the tasks.
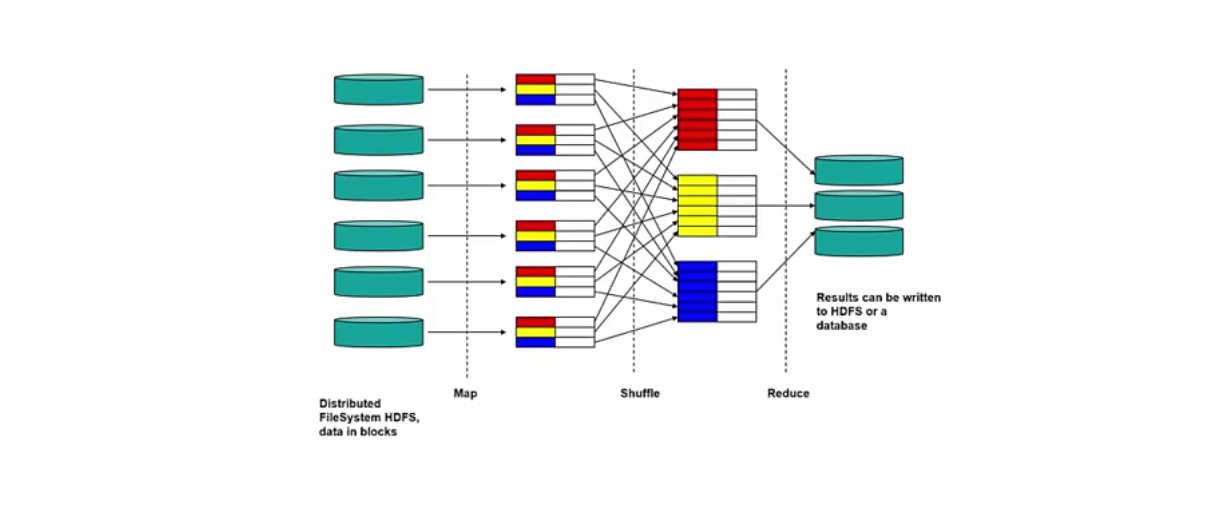
You may also like: Word Count Program With MapReduce and Java.
Mapper Phase
It is relatively a small program with a simple task. It is responsible for the implementation of the portion of input file data (mainly one block of one file). Interpreting, filtering, and transforming data is necessary in order to produce a stream of key-value pairs. One node is chosen to process data on the basis of the key. MapReduce transparently orchestrates all of this movement.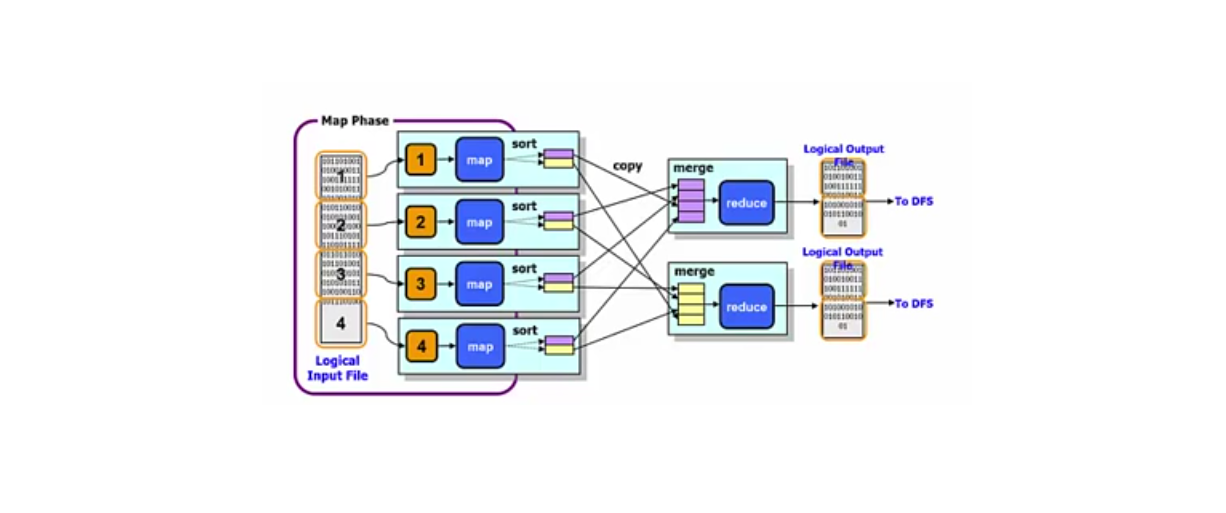
public static class Map extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,IntWritable> {
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
value.set(tokenizer.nextToken());
context.write(value, new IntWritable(1));
}
}
}
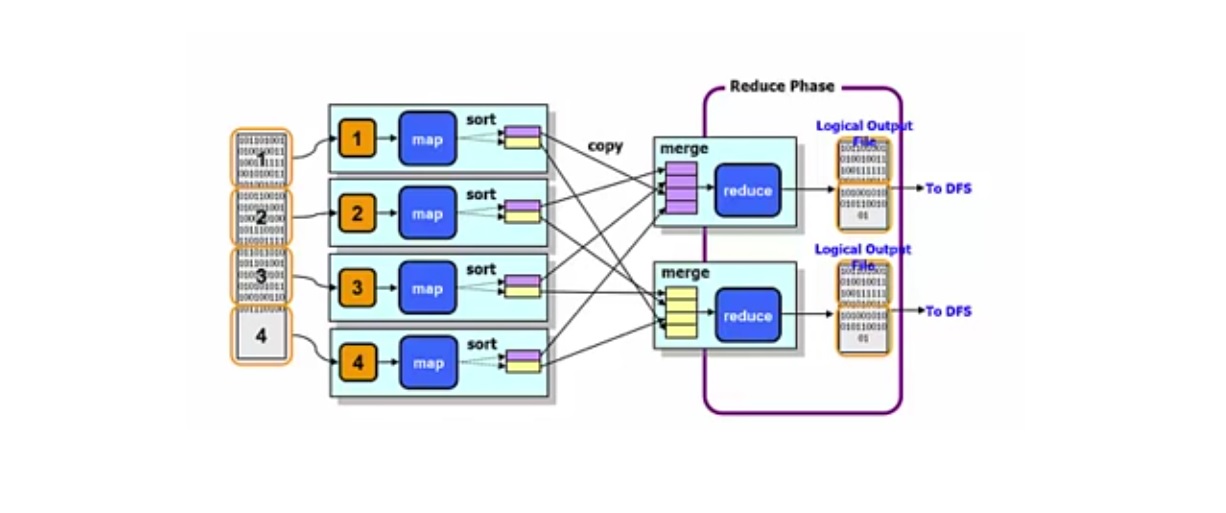
Reducer Phase
Reducer is a program that deals with an aggregation of all the values for the keys that they are responsible for. Each reducer typically writes output to its own file.
xxxxxxxxxx
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException {
int sum=0;
for(IntWritable x: values){
sum+=x.get();
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
Driver Class
xxxxxxxxxx
public class Counter{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf= new Configuration();
Job job = new Job(conf,"My Word Count Program");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
Path outputPath = new Path(args[1]);
//Configure the I/O path from the filesystem to the job
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
//delete the output path automatically from hdfs
outputPath.getFileSystem(conf).delete(outputPath);
//exit the job
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
Further Reading
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments