Asynchronous Communication With Queues and Microservices: A Perfect Combination?
In this article, we throw some light on what asynchronous messaging is all about and discuss why you should consider it for your microservices architectures.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this article, we throw some light on what asynchronous messaging is all about and discuss why you should consider it for your microservices architectures.
What You Will Learn
- What Asynchronous Communication is.
- Why We Need Asynchronous Communication.
- How Asynchronous Communication is implemented.
- Why should you consider using Asynchronous Communication for your microservices.
Best Practices With Cloud and Microservices
This is the last article in a series of six articles on best practices with cloud and microservices. The first five parts can be found here:
- The 12 Factor App: Best Practices in Cloud Native Applications and Microservices
- Microservices Architectures: Event Driven Approach
- Microservices Best Practices: Whey Do You Build a Vertical Slice?
- Microservices Artchitecture Best Practices: Messaging Queues
- Microservices Best Practices: Build an Archetype
What Is Synchronous Communication?
Consider the following example of a microservices architecture:
You have Microservice1 calling Microservice2, which in turn invokes Microservice3. Suppose that Microservice3 offers a simple web service functionality. So Microservice1 can send it a request for data over HTTP, and get back a response containing the requested data.
The communication that exists between these two microservices is called synchronous communication. Microservice1 sends the request, waits for the data to be returned, and then proceeds.
Drawbacks of Synchronous Communication
This mode of communication works well when the response arrives almost immediately. However, it puts restrictions on the microservices that are involved. In order that Microservice1 be available, Microservice2 also needs to be available.
In certain scenarios, synchronous communication might not even be user friendly.
Let's say Microservice2 is down. In that case, the user who submitted the request needs to be intimated about it. You don't always want to do that. In such situations, asynchronous communication provides a better alternative.
Asynchronous Communication
Have a look at the following application architecture:
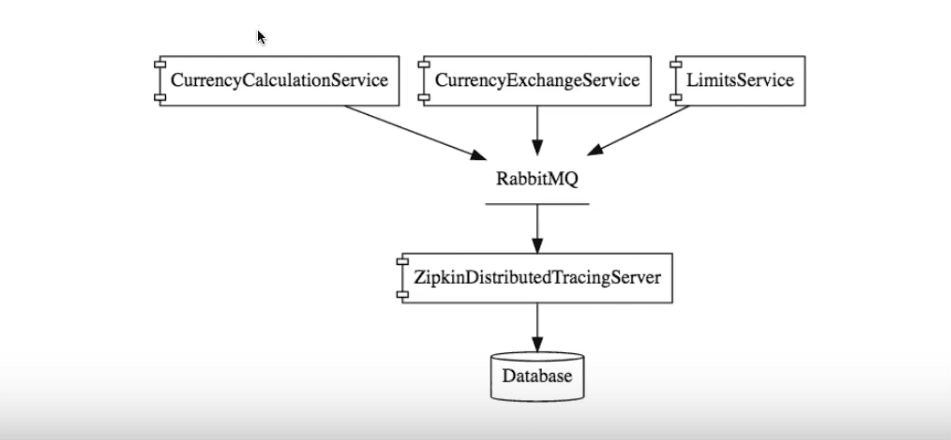
In the picture above, we make use of a ZipkinDistributedTracingServer. Different microservices send logs that are finally consolidated in the Zipkin Tracing Service. Each microservice puts its tracing information into the RabbitMQ message queue. The server processes messages as and when they come into the queue.
In this architecture, applications communicate through RabbitMQ. CurrencyCalculationService puts its own tracing information into RabbitMQ, and then forgets about it. It does not worry about the responses coming back to it.
Now, what would happen if the ZipkinDistributedTracingServer were to go down?
The services communicating with it would not worry one bit. They would continue sending messages to the queue. When the server comes back up, it resumes processing the messages present in the queue, and saves them to the database.
Advantages of Asynchronous Communication
Let's look at a few advantages of asynchronous communication:
- In a system that involves asynchronous messaging, the server does not need to be up and running all the time. Messages that are put into the message queue can be processed in batches, at a later time.
- Instead of a single instance of the tracing server processing the message queue, you could spawn multiple instances to lighten the load.
- If you use a modern version of a messaging queue, there is a good chance you get to use a replay feature. This helps in re-processing a message that initially threw an error.
- Asynchronous communication is great for systems that require eventual consistency.
The great thing is that as long as we fix the errors and reprocess the message, the users of services that initiated the requests with errors do not even need to know about them.
Limitations of Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication cannot be used if the processing needs to be real-time — i.e. if there is a hard constraint on the response time of a certain request.
Summary
In this article, we had a look at what asynchronous communication is all about. We started with a peek at synchronous communication, and saw that it puts constraints on applications and their availability. Asynchronous communication solves the problem by causing services to enqueue requests into a message queue. A server then processes them independently, often in batches.
Published at DZone with permission of Ranga Karanam, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments