Kafka Architecture: Log Compaction
This article on Kafka architecture talks goes over Kafka design and log compaction, its structure, and the log compaction process.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freethis post really picks off from our series on kafka architecture which includes kafka topics architecture , kafka producer architecture , kafka consumer architecture , and kafka ecosystem architecture .
this article is heavily inspired by the kafka section on design around log compaction . you can think of it as the cliff notes about kafka design around log compaction .
kafka can delete older records based on time or size of a log. kafka also supports log compaction for record key compaction. log compaction means that kafka will keep the latest version of a record and delete the older versions during a log compaction.
jean-paul azar works at cloudurable . cloudurable provides kafka training , kafka consulting , kafka support and helps setting up kafka clusters in aws .
kafka log compaction
log compaction retains at least the last known value for each record key for a single topic partition. compacted logs are useful for restoring state after a crash or system failure.
they are useful for in-memory services, persistent data stores, reloading a cache, etc. an important use case of data streams is to log changes to keyed, mutable data changes to a database table or changes to object in in-memory microservice.
log compaction is a granular retention mechanism that retains the last update for each key. a log compacted topic log contains a full snapshot of final record values for every record key not just the recently changed keys.
kafka log compaction allows downstream consumers to restore their state from a log compacted topic.
kafka log compaction structure
with a compacted log , the log has head and tail. the head of the compacted log is identical to a traditional kafka log. new records get appended to the end of the head.
all log compaction works at the tail of the log. only the tail gets compacted. records in the tail of the log retain their original offset when written after being rewritten with compaction cleanup .
kafka log compaction structure

kafka log compaction basics
all compacted log offsets remain valid, even if record at offset has been compacted away as a consumer will get the next highest offset.
kafka log compaction also allows for deletes. a message with a key and a null payload acts like a tombstone, a delete marker for that key. tombstones get cleared after a period. log compaction periodically runs in the background by re-copying log segments. compaction does not block reads and can be throttled to avoid impacting i/o of producers and consumers.
kafka log compaction process
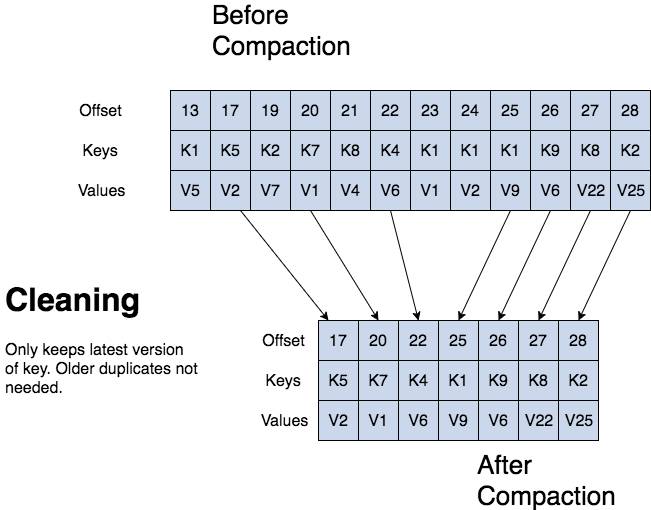
kafka log compaction cleaning
if a kafka consumer stays caught up to head of the log, it sees every record that is written.
topic config
min.compaction.lag.ms
gets used to guarantee a minimum period that must pass before a message can be compacted. the consumer sees all tombstones as long as the consumer reaches head of a log in a period less than the topic config
delete.retention.ms
(the default is 24 hours). log compaction will never re-order messages, just remove some. partition offset for a message never changes.
any consumer reading from the start of the log sees at least final state of all records in the order they were written.
kafka log cleaner
recall that a kafka topic has a log. a log is broken up into partitions and partitions are divided into segments which contain records which have keys and values.
the kafka log cleaner does log compaction. the log cleaner has a pool of background compaction threads. these threads recopy log segment files, removing older records whose key reappears recently in the log. each compaction thread chooses topic log that has the highest ratio of log head to log tail. then the compaction thread recopies the log from start to end removing records whose keys occur later in the log.
as the log cleaner cleans log partition segments, the segments get swapped into the log partition immediately replacing the older segments. this way compaction does not require double the space of the entire partition as additional disk space required is just one additional log partition segment - divide and conquer.
topic config for log compaction
to turn on compaction for a topic, use topic config
log.cleanup.policy=compact
.
to set a delay to start compacting records after they are written, use topic config
log.cleaner.min.compaction.lag.ms
. records won’t get compacted until after this period. the setting gives consumers time to get every record.
log compaction review
what are three ways kafka can delete records?
kafka can delete older records based on time or size of a log. kafka also supports log compaction for record key compaction.
what is log compaction good for?
since log compaction retains last known value it is a full snapshot of the latest records it is useful for restoring state after a crash or system failure for an in-memory service, a persistent data store, or reloading a cache. it allows downstream consumers to restore their state.
what is the structure of a compacted log? describe the structure.
with a compacted log, the log has head and tail. the head of the compacted log is identical to a traditional kafka log. new records get appended to the end of the head. all log compaction works at the tail of the compacted log.
after compaction, do log record offsets change? no.
what is a partition segment?
recall that a topic has a log. a topic log is broken up into partitions and partitions are divided into segment files which contain records which have keys and values. segment files allow for divide and conquer when it comes to log compaction. a segment file is part of the partition. as the log cleaner cleans log partition segments, the segments get swapped into the log partition immediately replacing the older segment files. this way compaction does not require double the space of the entire partition as additional disk space required is just one additional log partition segment.
jean-paul azar works at cloudurable . cloudurable provides kafka training , kafka consulting , kafka support and helps setting up kafka clusters in aws .
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments